Caspase activation, sialidase release and changes in sialylation pattern of recombinant human erythropoietin produced by CHO cells in batch and fed-batch cultures
- PMID: 19002897
- PMCID: PMC3449677
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-006-9016-5
Caspase activation, sialidase release and changes in sialylation pattern of recombinant human erythropoietin produced by CHO cells in batch and fed-batch cultures
Abstract
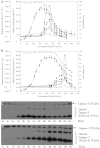
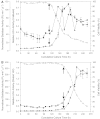
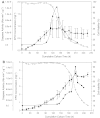
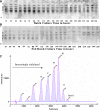
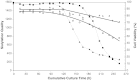
The activation of caspases represents a crucial turning point during a batch or a fed-batch culture of mammalian cells. It not only affects the quantity but also the quality of the recombinant glycoprotein produced. In this study, the activation of various caspases, the release of intracellular sialidase and the changes in sialylation pattern of a recombinant product, erythropoietin (EPO), in the culture medium were analyzed in both batch and fed-batch cultures. In both setups, all caspase activities peaked at the culture time point at which decline of cell viability was most pronounced. In addition, the release of intracellular lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was also tracked during these cultures. The increase in LDH activity in the medium coincided with the increase of intracellular caspase activities, the release of sialidase and the observed decline in cell viability, suggesting that the LDH activity in the medium can be used as an indirect indicator of apoptotic cell death in bioreactors. Isoelectric focusing (IEF) coupled with double blotting was employed to analyze the changes in sialylation pattern of the recombinant EPO. This assay resulted in a prompt resolution of secreted EPO isoforms in a time course format. IEF profile of batch culture showed relatively consistent product sialylation compared to fed-batch culture, which showed gradual band shifts towards the isoforms with fewer sialic acid as the culture progressed. These data provided a guideline for the optimal time point to terminate the culture and collect products in batch and fed-batch cultures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockout of sialidase and pro-apoptotic genes in Chinese hamster ovary cells enables the production of recombinant human erythropoietin in fed-batch cultures.Metab Eng. 2020 Jan;57:182-192. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2019.11.008. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Metab Eng. 2020. PMID: 31785386
-
Heat shock protein 27 overexpression in CHO cells modulates apoptosis pathways and delays activation of caspases to improve recombinant monoclonal antibody titre in fed-batch bioreactors.Biotechnol J. 2015 May;10(5):790-800. doi: 10.1002/biot.201400764. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25740626
-
HPCE monitoring of the N-glycosylation pattern and sialylation of murine erythropoietin produced by CHO cells in batch processes.Biotechnol Prog. 2004 May-Jun;20(3):864-71. doi: 10.1021/bp0343211. Biotechnol Prog. 2004. PMID: 15176893
-
Specific inhibition of caspase-8 and -9 in CHO cells enhances cell viability in batch and fed-batch cultures.Metab Eng. 2007 Sep-Nov;9(5-6):406-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2007.06.001. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Metab Eng. 2007. PMID: 17658284
-
Concomitant reduction of lactate and ammonia accumulation in fed-batch cultures: Impact on glycoprotein production and quality.Biotechnol Prog. 2018 Mar;34(2):494-504. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2607. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Biotechnol Prog. 2018. PMID: 29314777
Cited by
-
Investigation of purification process stresses on erythropoietin peptide mapping profile.Adv Biomed Res. 2015 May 29;4:114. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.157836. eCollection 2015. Adv Biomed Res. 2015. PMID: 26261816 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Engineering of Glycan Sialylation in Heterologous Systems.Molecules. 2021 Sep 30;26(19):5950. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195950. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting cell death pathways in fed-batch bioreactors.Biotechnol J. 2024 Jan;19(1):e2300257. doi: 10.1002/biot.202300257. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38038229 Free PMC article.
-
Galactose supplementation enhance sialylation of recombinant Fc-fusion protein in CHO cell: an insight into the role of galactosylation in sialylation.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Jul;31(7):1147-56. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1864-8. Epub 2015 May 1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25931375
-
Cross validation of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and lectin array for monitoring glycosylation in fed-batch glycoprotein production.Mol Biotechnol. 2012 Jul;51(3):272-82. doi: 10.1007/s12033-011-9465-8. Mol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22048797
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

