Future treatment strategies of aggressive pituitary tumors
- PMID: 19003539
- PMCID: PMC2712619
- DOI: 10.1007/s11102-008-0154-y
Future treatment strategies of aggressive pituitary tumors
Abstract
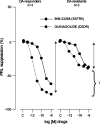
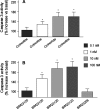
While surgery remains the first-line treatment of most aggressive pituitary adenomas, medical therapy is important as second-line or adjunctive therapy in a large proportion of patients. Dopamine agonists (DAs) are the best treatment for prolactinomas, but when DAs are not tolerated, new somatostatin receptor subtype 5 (SSTR(5)) inhibitors may offer an alternative in the future. Unfortunately, these are unlikely to be effective in DA-resistant prolactinomas. In acromegaly, the existing somatostatin analogs, octreotide and lanreotide, will remain the medical treatment of choice for the foreseeable future. There is an urgent need for medical therapies in Cushing's disease, and the SSTR(5) analogs could offer an effective treatment in a proportion of patients within the next few years. Finally, the medical management options for non-functioning pituitary adenomas are also very limited, and a new chimeric agent with activity towards dopamine receptors, SSTR(5) and SSTR(2) may help reduce adenoma recurrence in the future.
Figures
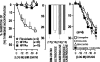
Similar articles
-
Treatment of pituitary tumors: somatostatin.Endocrine. 2005 Oct;28(1):93-100. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:28:1:093. Endocrine. 2005. PMID: 16311415 Review.
-
Pre-clinical and clinical experiences with novel somatostatin ligands: advantages, disadvantages and new prospects.J Endocrinol Invest. 2005;28(11 Suppl International):36-42. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005. PMID: 16625843 Review.
-
Multimodality treatment of pituitary adenomas.Clin Neurosurg. 2005;52:234-42. Clin Neurosurg. 2005. PMID: 16626076 No abstract available.
-
Medical approach to pituitary tumors.Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;124:303-16. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-59602-4.00020-4. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25248595 Review.
-
Expression and function of somatostatin receptor subtype 1 in human growth hormone secreting pituitary tumors deriving from patients partially responsive or resistant to long-term treatment with somatostatin analogs.Neuroendocrinology. 2004 Mar;79(3):142-8. doi: 10.1159/000077272. Epub 2004 Apr 16. Neuroendocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15103227 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
A case of fugitive acromegaly, initially presented as invasive prolactinoma.Endocrine. 2010 Aug;38(1):1-5. doi: 10.1007/s12020-010-9341-5. Epub 2010 Apr 24. Endocrine. 2010. PMID: 20960094
-
Differential circular RNA expression profiles of invasive and non-invasive non-functioning pituitary adenomas: A microarray analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jun;98(26):e16148. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016148. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31261542 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual Course of an Aggressive Pituitary Prolactinoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature.Case Rep Neurol. 2019 Apr 30;11(1):148-156. doi: 10.1159/000499702. eCollection 2019 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31320875 Free PMC article.
-
Nonfunctioning giant pituitary adenomas: Invasiveness and recurrence.Surg Neurol Int. 2015 Nov 26;6:179. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.170536. eCollection 2015. Surg Neurol Int. 2015. PMID: 26674325 Free PMC article.
-
Use of 111In-pentetreotide scintigraphy for diagnosis and management of resistant macroprolactinoma.Endocrine. 2018 Jun;60(3):532-534. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1486-z. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Endocrine. 2018. PMID: 29214441 No abstract available.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1210/jc.84.9.3268', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.84.9.3268'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10487698', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10487698/'}]}
- Jaquet P, Ouafik L, Saveanu A et al (1999) Quantitative and functional expression of somatostatin receptor subtypes in human prolactinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(9):3268–3276. doi:10.1210/jc.84.9.3268 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1210/jc.2003-031344', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-031344'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15070915', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15070915/'}]}
- Hofland LJ, van der Hoek J, van Koetsveld PM et al (2004) The novel somatostatin analog SOM230 is a potent inhibitor of hormone release by growth hormone- and prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(4):1577–1585. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031344 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1210/jc.83.9.3308', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.83.9.3308'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9745446', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9745446/'}]}
- Chaidarun SS, Swearingen B, Alexander JM (1998) Differential expression of estrogen receptor-beta (ER beta) in human pituitary tumors: functional interactions with ER alpha and a tumor-specific splice variant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(9):3308–3315. doi:10.1210/jc.83.9.3308 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1023/A:1009903603495', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009903603495'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11081186', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11081186/'}]}
- Kaptain GJ, Simmons NE, Alden TD, Lopes MB, Vance ML, Laws ER (1999) Estrogen receptors in prolactinomas: a clinico-pathological study. Pituitary 1(2):91–98. doi:10.1023/A:1009903603495 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1210/er.2005-9998', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2005-9998'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16705142', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16705142/'}]}
- Gillam MP, Molitch ME, Lombardi G, Colao A (2006) Advances in the treatment of prolactinomas. Endocr Rev 27(5):485–534. doi:10.1210/er.2005-9998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

