Neutrophils, but not lymphocytes or monocytes, infiltrate maternal systemic vasculature in women with preeclampsia
- PMID: 19003640
- PMCID: PMC2593156
- DOI: 10.1080/10641950801958067
Neutrophils, but not lymphocytes or monocytes, infiltrate maternal systemic vasculature in women with preeclampsia
Abstract
Objective: Leukocytes are activated in women with preeclampsia, but the class of leukocytes that infiltrates the maternal vasculature and, therefore, is most likely to cause vascular dysfunction is not known.
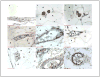
Methods: Subcutaneous fat biopsies were obtained at Cesarean section or abdominal surgery from 7 normal non-pregnant women, 7 women with normal pregnancies, and 7 women with preeclampsia. Tissues were immunohistochemically stained for CD14, a monocyte/macrophage antigen, CD99, a lymphocyte antigen, and CD66b, a neutrophil antigen.
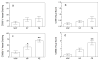
Results: CD14 stained cells were found infiltrated into fat tissue but were not present in vessels for any of the groups. CD99-stained cells were present in approximately 20% to 30% of vessels with no difference among groups. CD66b-stained cells were present in all groups with a significantly greater percentage of vessels stained for preeclamptic than normal pregnant or normal non-pregnant women (70 +/- 6 vs. 43 +/- 9 vs. 21 +/- 5%, respectively, p < 0.01). CD66b cells were the most abundant cell type that infiltrated vessels of preeclamptic women.
Conclusions: 1) A significantly greater number of neutrophils adhered to endothelium and infiltrated into the intimal space in the maternal systemic vasculature of preeclamptic women than in that of normal pregnant women or normal non-pregnant women; 2) No significant difference in lymphocyte infiltration was observed among the patient groups, and lymphocytes were present in much lower numbers than-neutrophils; 3) Monocytes/macrophages were found in fat tissue but not in vessels. We speculate that neutrophils are the class of leukocytes that cause the majority of vascular cell dysfunction in women with preeclampsia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophils infiltrate resistance-sized vessels of subcutaneous fat in women with preeclampsia.Hypertension. 2004 Jul;44(1):72-7. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000130483.83154.37. Epub 2004 May 17. Hypertension. 2004. PMID: 15148293
-
Systemic activation and vascular infiltration of neutrophils with term labor.J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2006 Sep;13(6):425-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsgi.2006.06.001. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2006. PMID: 16945759
-
Activation of NF-kappaB and expression of COX-2 in association with neutrophil infiltration in systemic vascular tissue of women with preeclampsia.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Jan;196(1):48.e1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2006.08.038. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007. PMID: 17240230
-
Pregnancy-specific expression of protease-activated receptor 1: a therapeutic target for prevention and treatment of preeclampsia?Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Feb;226(2S):S945-S953. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.11.1367. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 35177224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A leading role for the immune system in the pathophysiology of preeclampsia.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 Aug;94(2):247-57. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1112603. Epub 2013 Apr 30. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23633414 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation: Exploring Promising Pharmacological Strategies for the Treatment of Preeclampsia.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 9;17(5):605. doi: 10.3390/ph17050605. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput deep screening and identification of four peripheral leucocyte microRNAs as novel potential combination biomarkers for preeclampsia.J Perinatol. 2016 Apr;36(4):263-7. doi: 10.1038/jp.2015.192. Epub 2015 Dec 17. J Perinatol. 2016. PMID: 26675000 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil expression of cyclooxygenase 2 in preeclampsia.Reprod Sci. 2010 May;17(5):465-70. doi: 10.1177/1933719110361960. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Reprod Sci. 2010. PMID: 20220108 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Key Innate Immune Cells in Early- and Late-Onset Preeclampsia.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 18;11:1864. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01864. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Differential Expression of ERAP1/ERAP2 and Immune Cell Activation in Pre-eclampsia.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 10;11:396. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00396. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32210971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gervasi MT, Chaiworapongsa T, Pacora P, Naccasha N, Yoon BH, Maymon E, et al. Phenotypic and metabolic characteristics of monocytes and granulocytes in preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185:792–7. - PubMed
-
- Greer IA, Haddad NG, Dawes J, Johnstone FD, Calder AA. Neutrophil activation in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1989;96:978–982. - PubMed
-
- Haeger M, Unander M, Norder-Hansson B, Tylman M, Bengtsson A. Complement, neutrophil, and macrophage activation in women with severe preeclampsia and the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;79:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Tsukimori K, Maeda H, Ishida K, Nagata H, Koyanagi T, Nakano H. The superoxide generation of neutrophils in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 1993;81:536–540. - PubMed
-
- Sacks GP, Studena K, Sargent K, Redman CW. Normal pregnancy and preeclampsia both produce inflammatory changes in peripheral blood leukocytes akin to those of sepsis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:80–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
