Expression and developmental regulation of oxytocin (OT) and oxytocin receptors (OTR) in the enteric nervous system (ENS) and intestinal epithelium
- PMID: 19003903
- PMCID: PMC3097117
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.21872
Expression and developmental regulation of oxytocin (OT) and oxytocin receptors (OTR) in the enteric nervous system (ENS) and intestinal epithelium
Abstract
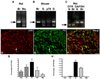
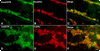
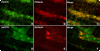
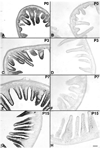
Although oxytocin (OT) and oxytocin receptor (OTR) are known for roles in parturition and milk let-down, they are not hypothalamus-restricted. OT is important in nurturing and opposition to stress. Transcripts encoding OT and OTR have been reported in adult human gut, and OT affects intestinal motility. We tested the hypotheses that OT is endogenous to the enteric nervous system (ENS) and that OTR signaling may participate in enteric neurophysiology. Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction confirmed OT and OTR transcripts in adult mouse and rat gut and in precursors of enteric neurons immunoselected from fetal rats. Enteric OT and OTR expression continued through adulthood but was developmentally regulated, peaking at postnatal day 7. Coincidence of the immunoreactivities of OTR and the neural marker Hu was 100% in the P3 and 71% in the adult myenteric plexus, when submucosal neurons were also OTR-immunoreactive. Co-localization with NeuN established that intrinsic primary afferent neurons are OTR-expressing. Because OTR transcripts and protein were detected in the nodose ganglia, OT signaling might also affect extrinsic primary afferent neurons. Although OT immunoreactivity was found only in approximately 1% of myenteric neurons, extensive OT-immunoreactive varicosities surrounded many others. Villus enterocytes were OTR-immunoreactive through postnatal day 17; however, by postnatal day 19, immunoreactivity waned to become restricted to crypts and concentrated at crypt-villus junctions. Immunoelectron microscopy revealed plasmalemmal OTR at enterocyte adherens junctions. We suggest that OT and OTR signaling might be important in ENS development and function and might play roles in visceral sensory perception and neural modulation of epithelial biology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oxytocin regulates gastrointestinal motility, inflammation, macromolecular permeability, and mucosal maintenance in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):G848-62. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00176.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25147234 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of macrophage polarization on the expression of the oxytocin signalling system in enteric neurons.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Nov 8;18(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02313-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34749758 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin hyperpolarizes cultured duodenum myenteric intrinsic primary afferent neurons by opening BK(Ca) channels through IP₃ pathway.J Neurochem. 2012 May;121(4):516-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07702.x. Epub 2012 Mar 20. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22356163
-
Molecular Basis of Oxytocin Receptor Signalling in the Brain: What We Know and What We Need to Know.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;35:3-29. doi: 10.1007/7854_2017_6. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28812263 Review.
-
Oxytocin/Oxytocin Receptor Signalling in the Gastrointestinal System: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10935. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010935. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-Specific Differences in Oxytocin Receptor Expression and Function for Parental Behavior.Gend Genome. 2017 Dec 1;1(4):142-166. doi: 10.1089/gg.2017.0017. Gend Genome. 2017. PMID: 32959027 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Acting and Selective Oxytocin Peptide Analogs Show Antidiabetic and Antiobesity Effects in Male Mice.J Endocr Soc. 2019 May 16;3(7):1423-1444. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00004. eCollection 2019 Jul 1. J Endocr Soc. 2019. PMID: 31286109 Free PMC article.
-
Hindbrain oxytocin receptors contribute to the effects of circulating oxytocin on food intake in male rats.Endocrinology. 2014 Aug;155(8):2845-57. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1148. Epub 2014 May 30. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24877632 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin Alleviates Colitis and Colitis-Associated Colorectal Tumorigenesis via Noncanonical Fucosylation.Research (Wash D C). 2024 Jul 8;7:0407. doi: 10.34133/research.0407. eCollection 2024. Research (Wash D C). 2024. PMID: 38979515 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin regulates gastrointestinal motility, inflammation, macromolecular permeability, and mucosal maintenance in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):G848-62. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00176.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25147234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adan RA, van Leeuwen FW, Sonnemans MA, Hoffman G, Verbalis JG, Burbach JP. The rat oxytocin receptor. cDNA cloning and immunocytochemical localization in brain, pituitary, mammary gland and uterus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;395:345–346. - PubMed
-
- Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ. A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:1276–1285. - PubMed
-
- Amico JA, Finn FM, Haldar J. Oxytocin and vasopressin are present in human and rat pancreas. Am J Med Sci. 1988;296:303–307. - PubMed
-
- Arciszewski MB, Ekblad E. Effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide and galanin on survival of cultured porcine myenteric neurons. Regul Pept. 2005;125:185–192. - PubMed
-
- Arciszewski MB, Sand E, Ekblad E. Vasoactive intestinal peptide rescues cultured rat myenteric neurons from lipopolysaccharide induced cell death. Regul Pept. 2008;146:218–223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

