Helicobacter infection decreases reproductive performance of IL10-deficient mice
- PMID: 19004370
- PMCID: PMC2707132
Helicobacter infection decreases reproductive performance of IL10-deficient mice
Abstract
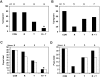
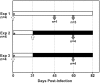
Infections with a variety of Helicobacter species have been documented in rodent research facilities, with variable effects on rodent health. Helicobacter typhlonius has been reported to cause enteric disease in immunodeficient and IL10(-/-) mice, whereas H. rodentium has only been reported to cause disease in immunodeficient mice coinfected with other Helicobacter species. The effect of Helicobacter infections on murine reproduction has not been well studied. The reproductive performance of C57BL/6 IL10(-/-) female mice intentionally infected with H. typhlonius, H. rodentium, or both was compared with that of age-matched uninfected controls or similarly infected mice that received antihelicobacter therapy. The presence of Helicobacter organisms in stool and relevant tissues was detected by PCR assays. Helicobacter infection of IL10(-/-) female mice markedly decreased pregnancy rates and pup survival. The number of pups surviving to weaning was greatest in noninfected mice and decreased for H. rodentium > H. typhlonius >> H. rodentium and H. typhlonius coinfected mice. Helicobacter organisms were detected by semiquantitative real-time PCR in the reproductive organs of a subset of infected mice. Treatment of infected mice with a 4-drug regimen consisting of amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole, and omeprazole increased pregnancy rates, and pup survival and dam fecundity improved. We conclude that infection with H. typhlonius, H. rodentium, or both decreased the reproductive performance of IL10(-/-) mice. In addition, antihelicobacter therapy improved fecundity and enhanced pup survival.
Figures
References
-
- American Veterinary Medical Association. 2007. AVMA guidelines on euthanasia (formerly Report of the AVMA Panel on Euthanasia): Jun 2007 update. Available from http://www.avma.org/issues/animal_welfare/euthanasia.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
