Daily rhythms of serum lipids in dogs: influences of lighting and fasting cycles
- PMID: 19004375
- PMCID: PMC2707135
Daily rhythms of serum lipids in dogs: influences of lighting and fasting cycles
Abstract
Circadian clocks organize a wide array of metabolic functions in a coherent daily schedule and ensure synchrony of this schedule with environmental rhythms. Daily rhythmicity of lipid metabolism occurs in rodents and ruminants. We examined daily level variations of serum lipids (nonesterified fatty acids [NEFA], triglycerides, phospholipids, total cholesterol and total lipids) in healthy dogs, particularly focusing on their temporal relationship to lighting and fasting cycles. Whereas serum NEFA levels did not change across the day, levels of total lipids, total cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides occurred in dogs maintained under 12:12-h light:dark cycles and fed a single meal daily. Only the rhythmic pattern of triglycerides responded to a 6 h delay in light onset, suggesting a cardinal role of a light-entrained circadian oscillator in its generation. To investigate whether temporal variations in serum lipids depend to physiological postprandial changes, we measured lipid levels in fasted dogs. Rhythms of total lipids, total cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides vanished when dogs were food-deprived, indicating that these rhythms are driven by the digestive process. Levels of serum NEFA patterns were significantly higher during fasting than after food intake. The increase of NEFA concentrations during fasting may reflect the mobilization of adipose tissue NEFA mediated by the decrease in insulin with its lypolitic effects. Elucidating the daily rhythmicity of lipid levels is fundamental to understanding the metabolism of the dog, an animal model frequently used for research in metabolic pathophysiology.
Figures
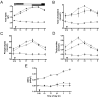
References
-
- Alila-Johansson A, Eriksson L, Soveri T, Laakso M. 2004. Daily and annual variations of free fatty acid, glycerol, and leptin plasma concentrations in goats (Capra hircus) under different photoperiods. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 138:119–131 - PubMed
-
- Alila-Johansson A, Eriksson L, Soveri T, Laakso ML. 2006. The daily rhythms of melatonin and free fatty acids in goats under varying photoperiods and constant darkness. Chronobiol Int 23:565–581 - PubMed
-
- Bailhache E, Nguyen P, Krempf M, Siliart B, Magot T, Ouguerram K. 2003. Lipoproteins abnormalities in obese insulin-resistant dogs. Metabolism 52:559–564 - PubMed
-
- Bartley JC. 1989. Lipid metabolism and its diseases. : Kaneko JJ.editor Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals. San Diego: Academic Press; p 106–141
-
- Bitman J, Wood DL, Lefcourt AM. 1990. Rhythms in cholesterol, cholesteryl esters, free fatty acids, and triglycerides in blood of lactating dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 73:948–955 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
