Complement Receptor 1: disease associations and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 19004497
- PMCID: PMC7125513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.09.026
Complement Receptor 1: disease associations and therapeutic implications
Abstract
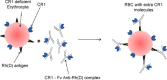
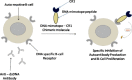
Exaggerated complement activation is a key event in the pathogenesis of a range of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Complement Receptor 1 (CR1) has emerged as a molecule of immense interest in gaining insight to the susceptibility, pathophysiology, diagnosis, prognosis and therapy of such diseases. This review brings forth a composite view of the current understanding on the structure, functions, genetics, disease associations and therapeutic implications of CR1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structure, genetic polymorphisms, expression and biological functions of complement receptor type 1 (CR1/CD35).Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2009;31(4):524-35. doi: 10.3109/08923970902845768. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2009. PMID: 19874218 Review.
-
Expression and role of CR1 and CR2 on B and T lymphocytes under physiological and autoimmune conditions.Mol Immunol. 2009 Sep;46(14):2767-73. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.05.181. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19559484 Review.
-
Association of complement receptor 1 (CR1, CD35, C3b/C4b receptor) density polymorphism with glomerulonephritis in Indian subjects.Mol Immunol. 2004 Apr;40(18):1325-32. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2003.12.003. Mol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15072851
-
Role of complement in the development of autoimmunity.Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2003;6:154-68. doi: 10.1159/000066860. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2003. PMID: 12408051 Review.
-
[The structure and role of CR1 complement receptor in physiology].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2010 Jan;28(163):79-83. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2010. PMID: 20369732 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Panel of Genetic Variations as a Potential Non-invasive Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2011 Aug;9(2):54-66. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2011.9.2.54. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 23429712 Free PMC article.
-
The immune adherence receptor CR1-like existed on porcine erythrocytes membrane.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 13;5:13290. doi: 10.1038/srep13290. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26268676 Free PMC article.
-
Up regulated complement and fc receptors in juvenile idiopathic arthritis and correlation with disease phenotype.J Clin Immunol. 2012 Jun;32(3):540-50. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9657-4. Epub 2012 Feb 11. J Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22328105
-
In vitro observation: the GFP-E. coli adhering to porcine erythrocytes can be removed by porcine alveolar macrophages.PeerJ. 2019 Mar 8;7:e6439. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6439. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30867982 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium falciparum field isolates use complement receptor 1 (CR1) as a receptor for invasion of erythrocytes.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2011 May;177(1):57-60. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2011.01.005. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21251929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahamson D.R., Fearon D.T. Endocytosis of the C3b receptor of complement within coated pits in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. Lab. Invest. 1983;48:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Adler S., Stahl R.A., Baker P.J., Chen Y.P., Pritzl P.M., Couser W.G. Biphasic effect of oxygen radicals on prostaglandin production by rat mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1987;252:F743–F749. - PubMed
-
- Arora M., Arora R., Tiwari S.C., Das N., Srivastava L.M. Expression of complement regulatory proteins in diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis. Lupus. 2000;9:127–131. - PubMed
-
- Arora V., Verma J., Dutta R., Marwah V., Kumar A., Das N. Reduced complement receptor 1 (CR1, CD35) transcription in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol. Immunol. 2004;41:449–456. - PubMed
-
- Arora V., Mondal A.M., Grover R., Kumar A., Chattopadhyay P., Das N. Modulation of CR1 transcript in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) by IFN-gamma and immune complex. Mol. Immunol. 2007;44:1722–1728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

