Up-regulation of cell surface Toll-like receptors on circulating gammadelta T-cells following burn injury
- PMID: 19004640
- PMCID: PMC3424612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.09.001
Up-regulation of cell surface Toll-like receptors on circulating gammadelta T-cells following burn injury
Abstract
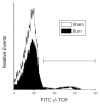
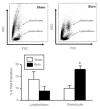
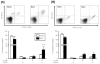
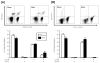
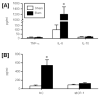
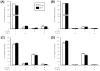
Burn injury is associated with profound inflammation and activation of the innate immune system involving gammadelta T-cells. Similarly, Toll-like receptors (TLR) are associated with activation of the innate immune response; however, it is unclear whether TLR expression is altered in gammadelta T-cells after major burn injury. To study this, male C57BL/6 mice were subjected to burn injury (25% TBSA) and 1 or 7 days thereafter, blood and spleen cells were isolated and subjected to FACs analysis for TLRs and other phenotypic markers (gammadelta TCR, alphabeta TCR, CD69, CD120b). A marked increase in the number of circulating gammadelta T-cells was observed at 24h post-burn (14% vs. 4%) and a higher percentage of these cells expressed TLR-2. TLR-4 expression was also increased post-burn, but to a lesser degree. These changes in TLR expression were not associated with altered CD69 or CD120b expression in gammadelta T-cells. The mobilization of, and increased TLR expression in, gammadelta T-cells was transient, as phenotypic changes were not evident at 7 days post-burn or in gammadelta T-cells from the circulation or spleen. The increases in TLR expression were not observed in alphabeta T-cells after burn injury. In conclusion, 24h after burn injury mobilization of gammadelta T-cells with increased TLR expression was observed. This finding suggests that this unique T-cell population is critical in the innate immune response to injury, possibly through the recognition of danger signals by TLRs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated skin γδ T-cells regulate T-cell infiltration of the wound site after burn.Innate Immun. 2015 Feb;21(2):140-50. doi: 10.1177/1753425913519350. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Innate Immun. 2015. PMID: 24412847
-
The role of gammadelta T cells in the regulation of neutrophil-mediated tissue damage after thermal injury.J Leukoc Biol. 2004 Sep;76(3):545-52. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0404219. Epub 2004 Jun 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15197233
-
The composition of T-cell subsets are altered in the burn wound early after injury.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 2;12(6):e0179015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179015. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28575063 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of γδ T cell responses by TLR ligands.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Jul;68(14):2357-70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0699-1. Epub 2011 May 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21560072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Th-17 Cells and γδ T-Cells in Modulating the Systemic Inflammatory Response to Severe Burn Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 3;18(4):758. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040758. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28368347 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The parasitic worm product ES-62 up-regulates IL-22 production by γδ T cells in the murine model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis.Inflamm Cell Signal. 2014;1(5):308. doi: 10.14800/ics.308. Inflamm Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 26594650 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia Induce Neurotoxic IL-17+ γδ T Cells Dependent on TLR2, TLR4, and TLR9 Activation.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 19;10(8):e0135898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135898. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26288016 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Relationship between Toll Like Receptors and Gamma Delta T Cell Responses.Front Immunol. 2014 Jul 31;5:366. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00366. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25132835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burn induces a Th-17 inflammatory response at the injury site.Burns. 2011 Jun;37(4):646-51. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2011.01.028. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Burns. 2011. PMID: 21353393 Free PMC article.
-
gammadelta T cells promote the maturation of dendritic cells during West Nile virus infection.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010 Jun 1;59(1):71-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00663.x. Epub 2010 Feb 17. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20337718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwacha MG. Macrophages and post-burn immune dysfunction. Burns. 2003;29:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Schneider DF, Glenn CH, Faunce DE. Innate lymphocyte subsets and their immunoregulatory roles in burn injury and sepsis. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:365–79. - PubMed
-
- Saffle JR, Sullivan JJ, Tuohig GM, Larson CM. Multiple organ failure in patients with thermal injury. Crit Care Med. 1993;21:1673–83. - PubMed
-
- Haas W, Pereira P, Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Ann Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

