Cross-repressive interactions between Lrig3 and netrin 1 shape the architecture of the inner ear
- PMID: 19004851
- PMCID: PMC2892390
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.029330
Cross-repressive interactions between Lrig3 and netrin 1 shape the architecture of the inner ear
Abstract
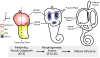
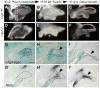
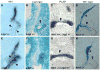
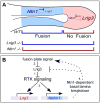
The sense of balance depends on the intricate architecture of the inner ear, which contains three semicircular canals used to detect motion of the head in space. Changes in the shape of even one canal cause drastic behavioral deficits, highlighting the need to understand the cellular and molecular events that ensure perfect formation of this precise structure. During development, the canals are sculpted from pouches that grow out of a simple ball of epithelium, the otic vesicle. A key event is the fusion of two opposing epithelial walls in the center of each pouch, thereby creating a hollow canal. During the course of a gene trap mutagenesis screen to find new genes required for canal morphogenesis, we discovered that the Ig superfamily protein Lrig3 is necessary for lateral canal development. We show that this phenotype is due to ectopic expression of the axon guidance molecule netrin 1 (Ntn1), which regulates basal lamina integrity in the fusion plate. Through a series of genetic experiments, we show that mutually antagonistic interactions between Lrig3 and Ntn1 create complementary expression domains that define the future shape of the lateral canal. Remarkably, removal of one copy of Ntn1 from Lrig3 mutants rescues both the circling behavior and the canal malformation. Thus, the Lrig3/Ntn1 feedback loop dictates when and where basement membrane breakdown occurs during canal development, revealing a new mechanism of complex tissue morphogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Chang W, Brigande JV, Fekete DM, Wu DK. The development of semicircular canals in the inner ear: role of FGFs in sensory cristae. Development. 2004;131:4201–11. - PubMed
-
- Fekete DM. Development of the vertebrate ear: insights from knockouts and mutants. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:263–9. - PubMed
-
- Fekete DM, Wu DK. Revisiting cell fate specification in the inner ear. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12:35–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

