Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease macrophage inflammatory gene expression by dexamethasone and the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor N-cyano-N'-(2-{[8-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-7-oxo-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d] pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}ethyl)guanidine (SB706504)
- PMID: 19004925
- PMCID: PMC2682286
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.142950
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease macrophage inflammatory gene expression by dexamethasone and the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor N-cyano-N'-(2-{[8-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-7-oxo-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d] pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}ethyl)guanidine (SB706504)
Abstract
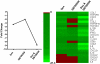
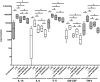
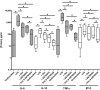
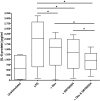
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling is known to be increased in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) macrophages. We have studied the effects of the p38 MAPK inhibitor N-cyano-N'-(2-{[8-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-7-oxo-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]-pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}ethyl)guanidine (SB706504) and dexamethasone on COPD macrophage inflammatory gene expression and protein secretion. We also studied the effects of combined SB706504 and dexamethasone treatment. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated monocyte derived macrophages (MDMs) and alveolar macrophages (AMs) were cultured with dexamethasone and/or SB706504. MDMs were used for gene array and protein studies, whereas tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha protein production was measured from AMs. SB706504 caused transcriptional inhibition of a range of cytokines and chemokines in COPD MDMs. The use of SB706504 combined with dexamethasone caused greater suppression of gene expression (-8.90) compared with SB706504 alone (-2.04) or dexamethasone (-3.39). Twenty-three genes were insensitive to the effects of both drugs, including interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-18, and chemokine (CC motif) ligand (CCL) 5. In addition, the chromosome 4 chemokine cluster members, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, and CXCL8, were all glucocorticoid-resistant. SB706504 significantly inhibited LPS-stimulated TNFalpha production from COPD and smoker AMs, with near-maximal suppression caused by combination treatment with dexamethasone. We conclude that SB706504 targets a subset of inflammatory macrophage genes and when used with dexamethasone causes effective suppression of these genes. SB706504 and dexamethasone had no effect on the transcription of a subset of LPS-regulated genes, including IL-1beta, IL-18, and CCL5, which are all known to be involved in the pathogenesis of COPD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition with a corticosteroid in alveolar macrophages from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Sep;338(3):732-40. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.180737. Epub 2011 May 24. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21610141
-
Different mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent cytokine responses in cells of the monocyte lineage.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Jan;324(1):306-12. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.127670. Epub 2007 Oct 5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 17921189
-
Reversal of corticosteroid insensitivity by p38 MAPK inhibition in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015 Feb 4;10:283-91. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S72403. eCollection 2015. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015. PMID: 25678784 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Asthma and COPD: Pathogenic Aspects and Potential Targeted Therapies.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Mar 23;15:1275-1284. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S300988. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33790539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p38 MAPK inhibitors, IKK2 inhibitors, and TNFα inhibitors in COPD.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;12(3):287-92. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2012.01.016. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22365729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
P38 MAPK and glucocorticoid receptor crosstalk in bronchial epithelial cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Mar;98(3):361-374. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01873-3. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 31974640 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting Edge: CLEC5A Mediates Macrophage Function and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathologies.J Immunol. 2016 Apr 15;196(8):3227-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500978. Epub 2016 Feb 29. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26927798 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of glucocorticoid receptor function in COPD lung macrophages using beclomethasone-17-monopropionate.PLoS One. 2013 May 21;8(5):e64257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064257. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23704983 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of a Cyanobacterial Fatty Acid Targeting the Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway.Mar Drugs. 2023 Oct 25;21(11):553. doi: 10.3390/md21110553. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37999377 Free PMC article.
-
FJU-C4, a new 2-pyridone compound, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation via p38MAPK and NF-κB in mice.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 23;8(12):e82877. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082877. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes PJ (2003) New concepts in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Annu Rev Med 54 113-129. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ (2006) Novel signal transduction modulators for the treatment of airway diseases. Pharmacol Ther 109 238-245. - PubMed
-
- Birrell MA, Wong S, McCluskie K, Catley MC, Hardaker EL, Haj-Yahia S, and Belvisi MG (2006) Second-generation inhibitors demonstrate the involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in post-transcriptional modulation of inflammatory mediator production in human and rodent airways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316 1318-1327. - PubMed
-
- Brook M, Tchen CR, Santalucia T, McIlrath J, Arthur JS, Saklatvala J, and Clark AR (2006) Posttranslational regulation of tristetraprolin subcellular localization and protein stability by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Mol Cell Biol 26 2408-2418. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

