The Mdm2 ubiquitin ligase enhances transcriptional activity of human papillomavirus E2
- PMID: 19004934
- PMCID: PMC2620916
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01551-08
The Mdm2 ubiquitin ligase enhances transcriptional activity of human papillomavirus E2
Abstract
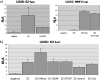
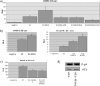
The regulation of human papillomavirus (HPV) gene expression by the E2 protein is a critical feature of the viral life cycle. Previous studies have shown an important role in transcription for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, but its role in HPV gene expression has not been addressed. We now show that HPV E2 requires an active proteasome for its optimal transcriptional activator function. This involves an interaction with the Mdm2 ubiquitin ligase, which together with E2 acts synergistically to activate the HPV type 16 promoter. We also show that HPV E2 recruits Mdm2 onto HPV promoter sequences, providing an explanation for this cooperative activity.
Figures


References
-
- Adhikary, S., F. Marinoni, A. Hock, E. Hulleman, N. Popov, R. Beier, S. Bernard, M. Quarto, M. Capra, S. Goettig, U. Kogel, M. Scheffner, K. Helin, and M. Eilers. 2005. The ubiquitin ligase HectH9 regulates transcriptional activation by Myc and is essential for tumor cell proliferation. Cell 123409-421. - PubMed
-
- Calabro, V., G. Mansueto, T. Parisi, M. Vivo, R. A. Calogero, and G. La Mantia. 2002. The human MDM2 oncoprotein increases the transcriptional activity and the protein level of the p53 homolog p63. J. Biol. Chem. 2772674-2681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

