African swine fever virus blocks the host cell antiviral inflammatory response through a direct inhibition of PKC-theta-mediated p300 transactivation
- PMID: 19004945
- PMCID: PMC2612362
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01663-08
African swine fever virus blocks the host cell antiviral inflammatory response through a direct inhibition of PKC-theta-mediated p300 transactivation
Abstract
During a viral infection, reprogramming of the host cell gene expression pattern is required to establish an adequate antiviral response. The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CREB binding protein (CBP) play a central role in this regulation by promoting the assembly of transcription enhancer complexes to specific promoters of immune and proinflammatory genes. Here we show that the protein A238L encoded by African swine fever virus counteracts the host cell inflammatory response through the control of p300 transactivation during the viral infection. We demonstrate that A238L inhibits the expression of the inflammatory regulators cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) by preventing the recruitment of p300 to the enhanceosomes formed on their promoters. Furthermore, we report that A238L inhibits p300 activity during the viral infection and that its amino-terminal transactivation domain is essential in the A238L-mediated inhibition of the inflammatory response. Importantly, we found that the residue serine 384 of p300 is required for the viral protein to accomplish its inhibitory function and that ectopically expressed PKC-theta completely reverts this inhibition, thus indicating that this signaling pathway is disrupted by A238L during the viral infection. Furthermore, we show here that A238L does not affect PKC-theta enzymatic activity, but the molecular mechanism of this viral inhibition relies on the lack of interaction between PKC-theta and p300. These findings shed new light on how viruses alter the host cell antiviral gene expression pattern through the blockade of the p300 activity, which represents a new and sophisticated viral mechanism to evade the inflammatory and immune defense responses.
Figures
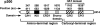



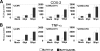




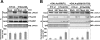
Similar articles
-
A238L inhibits NF-ATc2, NF-kappa B, and c-Jun activation through a novel mechanism involving protein kinase C-theta-mediated up-regulation of the amino-terminal transactivation domain of p300.J Immunol. 2008 Feb 15;180(4):2429-42. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2429. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18250452
-
The viral protein A238L inhibits TNF-alpha expression through a CBP/p300 transcriptional coactivators pathway.J Immunol. 2006 Jan 1;176(1):451-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.1.451. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16365438
-
Regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by viral A238L-mediated inhibition of p65/RelA acetylation and p300 transactivation.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(21):10487-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00862-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 17041221 Free PMC article.
-
Viral mechanisms involved in the transcriptional CBP/p300 regulation of inflammatory and immune responses.Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29(2):131-54. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i2.30. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19496744 Review.
-
Identification and utility of innate immune system evasion mechanisms of ASFV.Virus Res. 2013 Apr;173(1):87-100. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23165138 Review.
Cited by
-
The MGF300-2R protein of African swine fever virus is associated with viral pathogenicity by promoting the autophagic degradation of IKKα and IKKβ through the recruitment of TOLLIP.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 11;19(8):e1011580. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011580. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37566637 Free PMC article.
-
African Swine Fever Virus Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme Is an Immunomodulator Targeting NF-κB Activation.Viruses. 2021 Jun 17;13(6):1160. doi: 10.3390/v13061160. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34204411 Free PMC article.
-
African Swine Fever Virus Induces STAT1 and STAT2 Degradation to Counteract IFN-I Signaling.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 26;12:722952. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.722952. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34512601 Free PMC article.
-
African Swine Fever Virus and Host Response: Transcriptome Profiling of the Georgia 2007/1 Strain and Porcine Macrophages.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0193921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01939-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35019713 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in African swine fever virus molecular biology and host interactions contributing to new tools for control.J Virol. 2025 Jun 17;99(6):e0093224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00932-24. Epub 2025 May 9. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40340396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ait-Si-Ali, S., D. Carlisi, S. Ramirez, L. C. Upegui-Gonzalez, A. Duquet, P. Robin, B. Rudkin, A. Harel-Bellan, and D. Trouche. 1999. Phosphorylation by p44 MAP kinase/ERK1 stimulates CBP histone acetyl transferase activity in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 262157-162. - PubMed
-
- Arany, Z., D. Newsome, E. Oldread, D. M. Livingston, and R. Eckner. 1995. A family of transcriptional adaptor proteins targeted by the E1A oncoprotein. Nature 37481-84. - PubMed
-
- Arany, Z., W. R. Sellers, D. M. Livingston, and R. Eckner. 1994. E1A-associated p300 and CREB-associated CBP belong to a conserved family of coactivators. Cell 77799-800. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, A. J., T. Oehler, D. Wilhelm, P. Angel, and T. Kouzarides. 1995. Stimulation of c-Jun activity by CBP: c-Jun residues Ser63/73 are required for CBP induced stimulation in vivo and CBP binding in vitro. Oncogene 112509-2514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

