Increased extracellular pressure enhances cancer cell integrin-binding affinity through phosphorylation of beta1-integrin at threonine 788/789
- PMID: 19005162
- PMCID: PMC2637001
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00355.2008
Increased extracellular pressure enhances cancer cell integrin-binding affinity through phosphorylation of beta1-integrin at threonine 788/789
Abstract
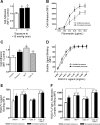
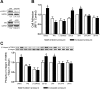
Increased extracellular pressure stimulates beta1-integrin-dependent cancer cell adhesion. We asked whether pressure-induced adhesion is mediated by changes in beta1-integrin binding affinity or avidity and whether these changes are phosphorylation dependent. We evaluated integrin affinity and clustering in human SW620 colon cancer cells by measuring differences in binding between soluble Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-Fc ligands and RGD-Fc-F(ab')2 multimeric complexes under ambient and 15-mmHg increased pressures. Phosphorylation of beta1-integrin S785 and T788/9 residues in SW620 and primary malignant colonocytes was assessed in parallel. We further used GD25-beta1-integrin-null murine fibroblasts stably transfected with either wild-type beta1A-integrin, S785A, TT788/9AA, or T788D mutants to investigate the role of beta1-integrin site-specific phosphorylation. SW620 binding of RGD-Fc-F(ab')2 multimeric complexes, but not soluble RGD-Fc ligands, was sensitive to integrin clustering. RGD-Fc ligand binding was significantly increased under elevated pressure, suggesting that pressure modulates beta1-integrin affinity. Pressure stimulated both beta1-integrin S785 and T788/9 phosphorylation. GD25-beta1A-integrin wild-type and S785A cells displayed an increase in adhesion to fibronectin under elevated pressure, an effect absent in beta1-integrin-null and TT788/9AA cells. T788D substitution significantly elevated basal cell adhesion but displayed no further increase under pressure. These results suggest pressure-induced cell adhesion is mediated by beta1-integrin T788/9 phosphorylation-dependent changes in integrin binding affinity.
Figures

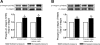



Similar articles
-
The effects of increased extracellular deformation, pressure, and integrin phosphorylation on fibroblast migration.J Surg Res. 2009 Sep;156(1):103-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2009.03.053. Epub 2009 May 3. J Surg Res. 2009. PMID: 19555977 Free PMC article.
-
The integrin beta1 subunit transmembrane domain regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Crk-associated substrate.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jun;15(6):2558-67. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-09-0700. Epub 2004 Mar 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15034138 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-actinin-1 phosphorylation modulates pressure-induced colon cancer cell adhesion through regulation of focal adhesion kinase-Src interaction.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Dec;293(6):C1862-74. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00118.2007. Epub 2007 Sep 26. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17898132
-
Mutational analysis of the potential phosphorylation sites in the cytoplasmic domain of integrin beta1A. Requirement for threonines 788-789 in receptor activation.J Cell Sci. 1998 Apr;111 ( Pt 8):1117-26. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.8.1117. J Cell Sci. 1998. PMID: 9512507
-
Neutrophil integrin affinity regulation in adhesion, migration, and bacterial clearance.Cell Adh Migr. 2013 Nov-Dec;7(6):476-81. doi: 10.4161/cam.27293. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2013. PMID: 24430200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of increased extracellular deformation, pressure, and integrin phosphorylation on fibroblast migration.J Surg Res. 2009 Sep;156(1):103-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2009.03.053. Epub 2009 May 3. J Surg Res. 2009. PMID: 19555977 Free PMC article.
-
Biological impact of mechanical stimuli on tumor metastasis.Cell Cycle. 2009 Mar 15;8(6):828-31. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.6.7940. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19229129 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome bioprofiles distinguish between M1 priming and activation states in human macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Apr;87(4):655-62. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0809570. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20007246 Free PMC article.
-
beta(1)-integrin mediates pressure-stimulated phagocytosis.Am J Surg. 2009 Nov;198(5):611-6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2009.07.006. Am J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19887187 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of platelet GPIIb/IIIa and alphavbeta3 integrins during HeLa cells adhesion, migration, and invasion to monolayer endothelium under static and dynamic shear flow.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009;2009:829243. doi: 10.1155/2009/829243. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19888429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barreuther MF, Grabel LB. The role of phosphorylation in modulating beta 1 integrin localization. Exp Cell Res 222: 10–15, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Basson MD, Yu CF, Herden-Kirchoff O, Ellermeier M, Sanders MA, Merrell RC, Sumpio BE. Effects of increased ambient pressure on colon cancer cell adhesion. J Cell Biochem 78: 47–61, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni G, Ma L, Blue ML, Hemler ME. Divalent cations and ligands induce conformational changes that are highly divergent among beta1 integrins. J Biol Chem 273: 6670–6678, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni G, Shih DT, Buck CA, Hemler ME. Monoclonal antibody 9EG7 defines a novel beta 1 integrin epitope induced by soluble ligand and manganese, but inhibited by calcium. J Biol Chem 270: 25570–25577, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Blaschke F, Stawowy P, Goetze S, Hintz O, Grafe M, Kintscher U, Fleck E, Graf K. Hypoxia activates beta(1)-integrin via ERK 1/2 and p38 MAP kinase in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296: 890–896, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

