Antithrombotic effects of targeting alphaIIbbeta3 signaling in platelets
- PMID: 19005179
- PMCID: PMC2668853
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-09-180687
Antithrombotic effects of targeting alphaIIbbeta3 signaling in platelets
Abstract
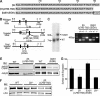
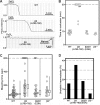
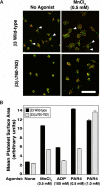
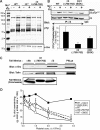
alphaIIbbeta3 interaction with fibrinogen promotes Src-dependent platelet spreading in vitro. To determine the consequences of this outside-in signaling pathway in vivo, a "beta3(Delta760-762)" knockin mouse was generated that lacked the 3 C-terminal beta3 residues (arginine-glycine-threonine [RGT]) necessary for alphaIIbbeta3 interaction with c-Src, but retained beta3 residues necessary for talin-dependent fibrinogen binding. beta3(Delta760-762) mice were compared with wild-type beta3(+/+) littermates, beta3(+/-) heterozygotes, and knockin mice where beta3 RGT was replaced by beta1 C-terminal cysteine-glycine-lysine (EGK) to potentially enable signaling by Src kinases other than c-Src. Whereas beta3(+/+), beta3(+/-) and beta3/beta1(EGK) platelets spread and underwent tyrosine phosphorylation normally on fibrinogen, beta3(Delta760-762) platelets spread poorly and exhibited reduced tyrosine phosphorylation of c-Src substrates, including beta3 (Tyr(747)). Unlike control mice, beta3(Delta760-762) mice were protected from carotid artery thrombosis after vessel injury with FeCl(3). Some beta3(Delta760-762) mice exhibited prolonged tail bleeding times; however, none demonstrated spontaneous bleeding, excess bleeding after surgery, fecal blood loss, or anemia. Fibrinogen binding to beta3(Delta760-762) platelets was normal in response to saturating concentrations of protease-activated receptor 4 or glycoprotein VI agonists, but responses to adenosine diphosphate were impaired. Thus, deletion of beta3 RGT disrupts c-Src-mediated alphaIIbbeta3 signaling and confers protection from arterial thrombosis. Consequently, targeting alphaIIbbeta3 signaling may represent a feasible antithrombotic strategy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pinning a tail on platelet thrombi.Blood. 2009 Apr 9;113(15):3395. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-12-193284. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19359414 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Fyn function in hemostasis and alphaIIbbeta3-integrin signaling.J Cell Sci. 2008 May 15;121(Pt 10):1641-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.014076. Epub 2008 Apr 22. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18430780 Free PMC article.
-
The Tyrosine Kinase c-Src Specifically Binds to the Active Integrin αIIbβ3 to Initiate Outside-in Signaling in Platelets.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 19;290(25):15825-15834. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.648428. Epub 2015 May 6. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25947380 Free PMC article.
-
The proline-rich tyrosine kinase Pyk2 regulates platelet integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling.J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Feb;11(2):345-56. doi: 10.1111/jth.12099. J Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23216754
-
Beta3 tyrosine phosphorylation in alphaIIbbeta3 (platelet membrane GP IIb-IIIa) outside-in integrin signaling.Thromb Haemost. 2001 Jul;86(1):246-58. Thromb Haemost. 2001. PMID: 11487013 Review.
-
Recent development of peptides from glycoproteins IIb (alphaIIb) and IIIa (beta3) that inhibit platelet fibrinogen binding.Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2005 Apr;3(2):99-103. doi: 10.2174/1568016053544345. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2005. PMID: 15853697 Review.
Cited by
-
JAM-A protects from thrombosis by suppressing integrin αIIbβ3-dependent outside-in signaling in platelets.Blood. 2012 Apr 5;119(14):3352-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-397398. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22271446 Free PMC article.
-
Toward correlating structure and mechanics of platelets.Cell Adh Migr. 2016 Sep 2;10(5):568-575. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1173803. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Cell Adh Migr. 2016. PMID: 27104281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, signal transduction, activation, and inhibition of integrin αIIbβ3.Thromb J. 2023 Feb 13;21(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12959-023-00463-w. Thromb J. 2023. PMID: 36782235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
uPAR isoform 2 forms a dimer and induces severe kidney disease in mice.J Clin Invest. 2019 Apr 2;129(5):1946-1959. doi: 10.1172/JCI124793. eCollection 2019 Apr 2. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30730305 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet integrin αIIbβ3: signal transduction, regulation, and its therapeutic targeting.J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Mar 7;12(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0709-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30845955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986;44:517–518. - PubMed
-
- Hynes R. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110:673–687. - PubMed
-
- Ma YQ, Yang J, Pesho MM, Vinogradova O, Qin J, Plow EF. Regulation of integrin αIIbβ3 activation by distinct regions of its cytoplasmic tails. Biochemistry. 2006;45:6656–6662. - PubMed
-
- Wegener KL, Partridge AW, Han J, et al. Structural basis of integrin activation by talin. Cell. 2007;128:171–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

