Dramatically reduced surface expression of NK cell receptor KIR2DS3 is attributed to multiple residues throughout the molecule
- PMID: 19005473
- PMCID: PMC3487464
- DOI: 10.1038/gene.2008.91
Dramatically reduced surface expression of NK cell receptor KIR2DS3 is attributed to multiple residues throughout the molecule
Abstract
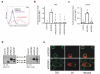
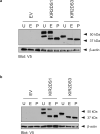
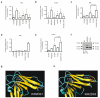
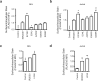
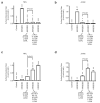
Using flow cytometry, fluorescent microscopy and examination of receptor glycosylation status, we demonstrate that an entire killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) locus (KIR2DS3)--assumed earlier to be surface expressed--appears to have little appreciable surface expression in transfected cells. This phenotype was noted for receptors encoded by three allelic variants including the common KIR2DS3*001 allele. Comparing the surface expression of KIR2DS3 with that of the better-studied KIR2DS1 molecule in two different cell lines, mutational analysis identified multiple polymorphic amino-acid residues that significantly alter the proportion of molecules present on the cell surface. A simultaneous substitution of five residues localized to the leader peptide (residues -18 and -7), second domain (residues 123 and 150) and transmembrane region (residue 234) was required to restore KIR2DS3 to the expression level of KIR2DS1. Corresponding simultaneous substitutions of KIR2DS1 to the KIR2DS3 residues resulted in a dramatically decreased surface expression. Molecular modeling was used to predict how these substitutions contribute to this phenotype. Alterations in receptor surface expression are likely to affect the balance of immune cell signaling impacting the characteristics of the response to pathogens or malignancy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Allelic variation of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS5 impacts glycosylation altering cell surface expression levels.Hum Immunol. 2014 Feb;75(2):124-8. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2013.11.012. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Hum Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24269691 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular domain alterations impact surface expression of stimulatory natural killer cell receptor KIR2DS5.Immunogenetics. 2008 Nov;60(11):655-67. doi: 10.1007/s00251-008-0322-2. Epub 2008 Aug 6. Immunogenetics. 2008. PMID: 18682925 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic HLA-C Receptors Balance the Functional Characteristics of KIR Haplotypes.J Immunol. 2015 Oct 1;195(7):3160-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501358. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26311903 Free PMC article.
-
From Chickens to Humans: The Importance of Peptide Repertoires for MHC Class I Alleles.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 14;11:601089. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.601089. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33381122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KIR specificity and avidity of standard and unusual C1, C2, Bw4, Bw6 and A3/11 amino acid motifs at entire HLA:KIR interface between NK and target cells, the functional and evolutionary classification of HLA class I molecules.Int J Immunogenet. 2019 Aug;46(4):217-231. doi: 10.1111/iji.12433. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Int J Immunogenet. 2019. PMID: 31210416 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of KIR genes and ligands in leukemia surveillance.Front Immunol. 2013 Feb 7;4:27. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00027. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23404428 Free PMC article.
-
Human-specific evolution of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor recognition of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Mar 19;367(1590):800-11. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0266. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22312047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The extensive polymorphism of KIR genes.Immunology. 2010 Jan;129(1):8-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03208.x. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20028428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thirty allele-level haplotypes centered around KIR2DL5 define the diversity in an African American population.Immunogenetics. 2010 Aug;62(8):491-8. doi: 10.1007/s00251-010-0458-8. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Immunogenetics. 2010. PMID: 20585770 Free PMC article.
-
Allelic variation of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS5 impacts glycosylation altering cell surface expression levels.Hum Immunol. 2014 Feb;75(2):124-8. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2013.11.012. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Hum Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24269691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Hsu KC, Chida S, Dupont B, Geraghty DE. The killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genomic region: gene-order, haplotypes and allelic polymorphism. Immunological Reviews. 2002;190(1):40–52. - PubMed
-
- Katz G, Markel G, Mizrahi S, Arnon TI, Mandelboim O. Recognition of HLA-Cw4 but not HLA-Cw6 by the NK cell receptor killer cell Ig-like receptor two-domain short tail number 4. J Immunol. 2001;166:7260–7267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

