GammaH2AX and cancer
- PMID: 19005492
- PMCID: PMC3094856
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc2523
GammaH2AX and cancer
Abstract
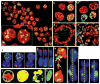
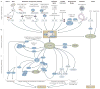
Histone H2AX phosphorylation on a serine four residues from the carboxyl terminus (producing gammaH2AX) is a sensitive marker for DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). DSBs may lead to cancer but, paradoxically, are also used to kill cancer cells. Using gammaH2AX detection to determine the extent of DSB induction may help to detect precancerous cells, to stage cancers, to monitor the effectiveness of cancer therapies and to develop novel anticancer drugs.
Figures

References
-
- McKinnon PJ, Caldecott KW. DNA strand break repair and human genetic disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007;8:37–55. - PubMed
-
- Jeggo PA, Lobrich M. DNA double-strand breaks: their cellular and clinical impact? Oncogene. 2007;26:7717–7719. - PubMed
-
- O’Driscoll M, Gennery AR, Seidel J, Concannon P, Jeggo PA. An overview of three new disorders associated with genetic instability: LIG4 syndrome, RS-SCID and ATR–Seckel syndrome. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:1227–1235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

