Activation of p16 gene silenced by DNA methylation in cancer cells by phosphoramidate derivatives of 2'-deoxyzebularine
- PMID: 19006382
- PMCID: PMC2659950
- DOI: 10.1021/jm8005965
Activation of p16 gene silenced by DNA methylation in cancer cells by phosphoramidate derivatives of 2'-deoxyzebularine
Abstract
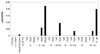
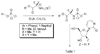
We report herein the application of the phosphoramidate ProTide technology to improve the metabolism of the DNA methytransferase inhibitor, zebularine (Z). Zebularine is a riboside that must undergo a complex metabolic transformation before reaching the critical 2'-deoxyzebularine 5'-triphosphate (dZTP). Because 2'-deoxyzebularine (dZ) is not phosphorylated and therefore inactive, the ProTide strategy was employed to bypass the lack of phosphorylation of dZ and the inefficient reduction of zebularine 5'-diphosphate by ribonucleotide-diphosphate reductase required for zebularine. Several compounds were identified as more potent inhibitors of DNA methylation and stronger inducers of p16 tumor suppressor gene than zebularine. However, their activity was dependent on the administration of thymidine to overcome the potent inhibition of thymidylate synthase (TS) and deoxycytidine monophosphate (dCMP) deaminase by dZMP, which deprives cells of essential levels of thymidine. Intriguingly, the activity of the ProTides was cell line-dependent, and activation of p16 was manifest only in Cf-Pac-1 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of DNA methylation and reactivation of silenced genes by zebularine.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003 Mar 5;95(5):399-409. doi: 10.1093/jnci/95.5.399. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. PMID: 12618505
-
Continuous zebularine treatment effectively sustains demethylation in human bladder cancer cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;24(3):1270-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.3.1270-1278.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14729971 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced growth inhibition by combined DNA methylation/HDAC inhibitors in lung tumor cells with silenced CDKN2A.Int J Oncol. 2010 Oct;37(4):963-71. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000747. Int J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20811718 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoramidates and phosphonamidates (ProTides) with antiviral activity.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2018 Jan-Dec;26:2040206618775243. doi: 10.1177/2040206618775243. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29792071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aryloxy phosphoramidate triesters: a technology for delivering monophosphorylated nucleosides and sugars into cells.ChemMedChem. 2009 Nov;4(11):1779-91. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200900289. ChemMedChem. 2009. PMID: 19760699 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic inhibitor zebularine activates ear pinna wound closure in the mouse.EBioMedicine. 2019 Aug;46:317-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Jul 11. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31303499 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagen Synergy: Hypermutability Generated by Specific Pairs of Base Analogs.J Bacteriol. 2016 Sep 22;198(20):2776-83. doi: 10.1128/JB.00391-16. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27457718 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic therapy for breast cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(7):4465-87. doi: 10.3390/ijms12074465. Epub 2011 Jul 11. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21845090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Zebularine on p16INK4a, p14ARF, p15INK4b, and DNA Methyltransferase 1 Gene Expression, Cell Growth Inhibition, and Apoptosis Induction in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma PLC/PRF5 and Pancreatic Cancer PA-TU-8902 Cell Lines.Iran J Pharm Res. 2020 Fall;19(4):193-202. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.112223.13614. Iran J Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 33841535 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of nucleoside phosphate and phosphonate prodrugs.Chem Rev. 2014 Sep 24;114(18):9154-218. doi: 10.1021/cr5002035. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 25144792 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baylin SB, Ohm JE. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer - a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Baylin SB. DNA methylation and gene silencing. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005;2:S4–S11. - PubMed
-
- Yoo CB, Jones PA. Epigenetic therapy of cancer: past, present and future. Nat. Rev.Drug Disc. 2006;5:37–50. - PubMed
-
- Cheng JC, Matsen CB, Gonzalez FA, Ye W, Greer S, Marquez VE, Jones PA, Selker EU. Inhibition of DNA methylation and reactivation of silenced genes by zebularine. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003;95:399–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

