A large kindred with X-linked neutropenia with an I294T mutation of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome gene
- PMID: 19006568
- PMCID: PMC3125974
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07416.x
A large kindred with X-linked neutropenia with an I294T mutation of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome gene
Abstract
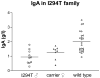
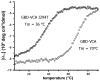
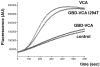
X-linked neutropenia (XLN, OMIM #300299) is a rare form of severe congenital neutropenia. It was originally described in a three-generation family with five affected members that had an L270P mutation in the GTP-ase binding domain (GBD) of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) [Devriendt et al (2001) Nature Genetics, Vol. 27, 313-317]. Here, we report and describe a large three-generation family with XLN, with 10 affected males and eight female carriers. A c.882T>C mutation was identified in the WAS gene, resulting in an I294T mutation. The infectious course is variable and mild in view of the profound neutropenia. In addition to the original description, low-normal IgA levels, low to low-normal platelet counts and reduced natural killer (NK)-cell counts also appear as consistent XLN features. However, inverted CD4/CD8 ratios were not found in this family, nor were cases identified with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukaemia. Female carriers exhibited a variable attenuated phenotype. Like L270P WASP, I294T WASP is constitutively active towards actin polymerization. In conclusion, this largest XLN kindred identified to date provides new independent genetic evidence that mutations disrupting the auto-inhibitory GBD of WASP are the cause of XLN. Reduced NK cells, low to low normal platelet counts and low to low-normal IgA levels are also features of XLN.
Figures
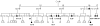
References
-
- Ancliff PJ, Blundell MP, Cory GO, Calle Y, Worth A, Kempski H, Burns S, Jones GE, Sinclair J, Kinnon C, Hann IM, Gale RE, Linch DC, Thrasher AJ. Two novel activating mutations in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein result in congenital neutropenia. Blood. 2006;108:2182–2189. - PubMed
-
- Bain B. Blood cells, a practical guide. Blackwell Science Ltd; London: 1995.
-
- Beel K, Schollen E, Uyttebroeck A, Verhoef G, Demuynck H, Devriendt K, Vandenberghe P. Gain-of-Function WASP Mutations in Pediatric and Adult Patients with Myelodysplasia or AML. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006;108:4516.
-
- Busque L, Mio R, Mattioli J, Brais E, Blais N, Lalonde Y, Maragh M, Gilliland DG. Nonrandom X-inactivation patterns in normal females: lyonization ratios vary with age. Blood. 1996;88:59–65. - PubMed
-
- Carrel L, Willard HF. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature. 2005;434:400–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

