IRAK-4- and MyD88-dependent pathways are essential for the removal of developing autoreactive B cells in humans
- PMID: 19006693
- PMCID: PMC2666307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.09.015
IRAK-4- and MyD88-dependent pathways are essential for the removal of developing autoreactive B cells in humans
Abstract
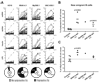
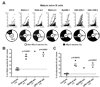
Most autoreactive B cells are normally counterselected during early B cell development. To determine whether Toll-like receptors (TLRs) regulate the removal of autoreactive B lymphocytes, we tested the reactivity of recombinant antibodies from single B cells isolated from patients deficient for interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK-4), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), and UNC-93B. Indeed, all TLRs except TLR3 require IRAK-4 and MyD88 to signal, and UNC-93B-deficient cells are unresponsive to TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9. All patients suffered from defective central and peripheral B cell tolerance checkpoints, resulting in the accumulation of large numbers of autoreactive mature naive B cells in their blood. Hence, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 may prevent the recruitment of developing autoreactive B cells in healthy donors. Paradoxically, IRAK-4-, MyD88-, and UNC-93B-deficient patients did not display autoreactive antibodies in their serum or develop autoimmune diseases, suggesting that IRAK-4, MyD88, and UNC-93B pathway blockade may thwart autoimmunity in humans.
Figures





Comment in
-
An innate path to human B cell tolerance.Immunity. 2008 Nov 14;29(5):667-9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.10.001. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 19006689 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
IgM+IgD+CD27+ B cells are markedly reduced in IRAK-4-, MyD88-, and TIRAP- but not UNC-93B-deficient patients.Blood. 2012 Dec 13;120(25):4992-5001. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-440776. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Blood. 2012. PMID: 23002119 Free PMC article.
-
Human Toll-like receptor-dependent induction of interferons in protective immunity to viruses.Immunol Rev. 2007 Dec;220(1):225-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00564.x. Immunol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17979850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An innate path to human B cell tolerance.Immunity. 2008 Nov 14;29(5):667-9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.10.001. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 19006689 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase (IRAK) Signaling in Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Induced Primary Effusion Lymphoma.J Virol. 2020 May 4;94(10):e02123-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02123-19. Print 2020 May 4. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32161170 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental and natural infections in MyD88- and IRAK-4-deficient mice and humans.Eur J Immunol. 2012 Dec;42(12):3126-35. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242683. Eur J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23255009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The establishment of early B cell tolerance in humans: lessons from primary immunodeficiency diseases.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Dec;1246:1-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06347.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 22236425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MyD88 controls human metapneumovirus-induced pulmonary immune responses and disease pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2013 Sep;176(1-2):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23845303 Free PMC article.
-
RNA mediated Toll-like receptor stimulation in health and disease.RNA Biol. 2012 Jun;9(6):828-42. doi: 10.4161/rna.20206. Epub 2012 May 23. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22617878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cup runneth over: lessons from the ever-expanding pool of primary immunodeficiency diseases.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Sep;13(9):635-48. doi: 10.1038/nri3493. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23887241 Review.
-
Flow Cytometry Contributions for the Diagnosis and Immunopathological Characterization of Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases With Immune Dysregulation.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 26;10:2742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02742. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31849949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Baccala R, Hoebe K, Kono DH, Beutler B, Theofilopoulos AN. TLR-dependent and TLR-independent pathways of type I interferon induction in systemic autoimmunity. Nat Med. 2007;13:543–551. - PubMed
-
- Berland R, Fernandez L, Kari E, Han JH, Lomakin I, Akira S, Wortis HH, Kearney JF, Ucci AA, Imanishi-Kari T. Toll-like receptor 7-dependent loss of B cell tolerance in pathogenic autoantibody knockin mice. Immunity. 2006;25:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi NL, Onai N, Lanzavecchia A. A role for Toll-like receptors in acquired immunity: up-regulation of TLR9 by BCR triggering in naive B cells and constitutive expression in memory B cells. Blood. 2003;101:4500–4504. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature. 2004;430:257–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

