Experience-dependent epigenetic modifications in the central nervous system
- PMID: 19006788
- PMCID: PMC3090137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.09.002
Experience-dependent epigenetic modifications in the central nervous system
Abstract
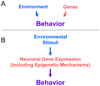
This mini-review describes recent discoveries demonstrating that experience can drive the production of epigenetic marks in the adult nervous system and that the experience-dependent regulation of epigenetic molecular mechanisms in the mature central nervous system participates in the control of gene transcription underlying the formation of long-term memories. In the mammalian experimental systems investigated thus far, epigenetic mechanisms have been linked to associative fear conditioning, extinction of learned fear, and hippocampus-dependent spatial memory formation. Intriguingly, in one experimental system epigenetic marks at the level of chromatin structure (histone acetylation) have been linked to the recovery of memories that had seemed to be "lost" (i.e., not available for recollection). Environmental enrichment has long been known to have positive effects on memory capacity, and recent studies have suggested that these effects are at least partly due to the recruitment of epigenetic mechanisms by environmental enrichment. Finally, an uncoupling of signal transduction pathways from the regulation of epigenetic mechanisms in the nucleus has been implicated in the closure of developmental critical periods. Taken together, these eclectic findings suggest a new perspective on experience-dependent dynamic regulation of epigenetic mechanisms in the adult nervous system and their relevance to biological psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Sweatt receives grant funding from the NIH, Evelyn F. McKnight Brain Research Foundation, the Rotary Clubs CART fund, and NARSAD. Dr. Sweatt reports no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. The author also wishes to thank Felecia Hester for her assistance in preparing this review.
Figures
References
-
- Waddington CH. The Strategy of the Genes. New York: MacMillan; 1957.
-
- Okano M, Xie S, Li E. Cloning and characterization of a family of novel mammalian DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nat Genet. 1998;19:219–220. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, et al. Direct identification of the active-site nucleophile in a DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1991;30:11018–11025. - PubMed
-
- Santi DV, Garrett CE, Barr PJ. On the mechanism of inhibition of DNA-cytosine methyltransferases by cytosine analogs. Cell. 1983;33:9–10. - PubMed
-
- Bird AP. Use of restriction enzymes to study eukaryotic DNA methylation: II. The symmetry of methylated sites supports semi-conservative copying of the methylation pattern. J Mol Biol. 1978;118:49–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

