Complex assembly on the human CYP17 promoter
- PMID: 19007851
- PMCID: PMC2754694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.10.006
Complex assembly on the human CYP17 promoter
Abstract
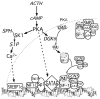
Optimal steroid hormone biosynthesis occurs via the integration of multiple regulatory processes, one of which entails a coordinate increase in the transcription of all genes required for steroidogenesis. In the human adrenal cortex adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) activates a signaling cascade that promotes the dynamic assembly of protein complexes on the promoters of steroidogenic genes. For CYP17, multiple transcription factors, including steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1), GATA-6, and sterol regulatory binding protein 1 (SREBP1), are recruited to the promoter during activated transcription. The ability of these factors to increase CYP17 mRNA expression requires the formation of higher order coregulatory complexes, many of which contain enzymatic activities that post-translationally modify both the transcription factors and histones. We discuss the mechanisms by which transcription factors and coregulatory proteins regulate CYP17 transcription and summarize the role of kinases, phosphatases, acetyltransferases, and histone deacetylases in controlling CYP17 mRNA expression.
Figures
References
-
- Auchus RJ, Lee TC, Miller WL. Cytochrome b5 augments the 17,20 lyase activity of human P450c17 without direct electron transfer. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:3158–3165. - PubMed
-
- Bakke M, Lund J. Mutually exclusive interactions of two nuclear orphan receptors determine activity of a cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate-responsive sequence in the bovine CYP17 gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1995a;9:327–339. - PubMed
-
- Bassett MH, Suzuki T, Sasano H, De Vries CJ, Jimenez PT, Carr BR, Rainey WE. The orphan nuclear receptor NGFIB regulates transcription of 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Implications for the control of adrenal functional zonation. J Biol Chem. 2004a;279:37622–37630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

