Expression of a 12-kb promoter element derived from the zebrafish enolase-2 gene in the zebrafish visual system
- PMID: 19007858
- PMCID: PMC2922958
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.10.101
Expression of a 12-kb promoter element derived from the zebrafish enolase-2 gene in the zebrafish visual system
Abstract
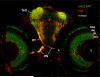
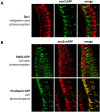
We recently cloned the zebrafish neuronal enolase-2 gene and showed that a 12-kb eno2 promoter element was sufficient to drive transgene expression widely in CNS neurons in vivo from 48h post-fertilization through adulthood. The aim of the present study was to establish the expression pattern of the 12-kb eno2 promoter element in the zebrafish visual system. Endogenous eno2 mRNA was detected in the developing retina from 2 days post-fertilization (dpf), and by 12dpf was localized to the retinal ganglion cell, inner and outer nuclear layers. Similar to endogenous eno2, GFP expression in the retina of Tg(eno2:GFP) larvae was first evident at 2dpf, and by 12dpf intense GFP expression was seen in the retinal ganglion cell and photoreceptor layers, with weaker expression in the inner nuclear layer. We identified cell types expressing the eno2 promoter element by using two complementary strategies: (i) double label immunofluorescence analysis of Tg(eno2:GFP) zebrafish, and (ii) generation of double transgenic zebrafish expressing red fluorescent protein under transcriptional control of the 12-kb eno2 promoter and GFP under a rod- or cone-specific promoter. The 12-kb eno2 promoter was expressed in retinal ganglion cells, amacrine cells, including a subset that co-expressed tyrosine hydroxylase, and rod photoreceptors. These data suggest that abnormalities of vision should be sought in transgenic models of diseases generated using this promoter. Owing to the specific expression of fluorescent reporters in neuronal subpopulations, Tg(eno2:GFP) and Tg(eno2:mRFP) zebrafish may be useful for studies of retinal lamination, neuronal differentiation and synapse formation in the visual system.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(19):6501-16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm608. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17897967 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting retinal dopaminergic neurons in tyrosine hydroxylase-driven green fluorescent protein transgenic zebrafish.Mol Vis. 2008;14:2475-83. Epub 2008 Dec 26. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 19112533 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of green fluorescent protein-expressing retinal cells in CD 44-transgenic mice.Neuroscience. 2007 Feb 9;144(3):1087-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.061. Epub 2006 Dec 8. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17161542 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish Tg(7.2mab21l2:EGFP)ucd2 transgenics reveal a unique population of retinal amacrine cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Mar 1;52(3):1613-21. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5376. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21051702 Free PMC article.
-
Purpurin is a key molecule for cell differentiation during the early development of zebrafish retina.Brain Res. 2009 Dec 11;1302:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.09.020. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19748496
Cited by
-
Neural innervation as a potential trigger of morphological color change and sexual dimorphism in cichlid fish.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 23;10(1):12329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69239-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32704058 Free PMC article.
-
Different mechanisms regulate expression of zebrafish myelin protein zero (P0) in myelinating oligodendrocytes and its induction following axonal injury.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 29;289(35):24114-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.545426. Epub 2014 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25028515 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of functional recovery in a larval zebrafish model of spinal cord injury.J Neurosci Res. 2022 Nov;100(11):2044-2054. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25118. Epub 2022 Aug 20. J Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 35986577 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoptogenetic ablation of neuronal mitochondria in vivo with spatiotemporal precision and controllable severity.Elife. 2020 Mar 17;9:e51845. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51845. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32180546 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish models of Tauopathy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Mar;1812(3):353-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.09.004. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20849952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

