A20: central gatekeeper in inflammation and immunity
- PMID: 19008218
- PMCID: PMC2659177
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R800032200
A20: central gatekeeper in inflammation and immunity
Abstract
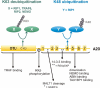
Inappropriate functioning of the immune system is linked to immune deficiency, autoimmune disease, and cancer. It is therefore not surprising that intracellular immune signaling pathways are tightly controlled. One of the best studied transcription factors in immune signaling is NF-kappaB, which is activated by multiple receptors and regulates the expression of a wide variety of proteins that control innate and adaptive immunity. A20 is an early NF-kappaB-responsive gene that encodes a ubiquitin-editing protein that is involved in the negative feedback regulation of NF-kappaB signaling. Here, we discuss the mechanism of action of A20 and its role in the regulation of inflammation and immunity.
Figures

References
-
- Dixit, V. M., Green, S., Sarma, V., Holzman, L. B., Wolf, F. W., O'Rourke, K., Ward, P. A., Prochownik, E. V., and Marks, R. M. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265 2973–2978 - PubMed
-
- Beyaert, R., Heyninck, K., and Van Huffel, S. (2000) Biochem. Pharmacol. 60 1143–1151 - PubMed
-
- Opipari, A. W., Jr., Hu, H. M., Yabkowitz, R., and Dixit, V. M. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267 12424–12427 - PubMed
-
- Karin, M., and Greten, F. R. (2005) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5 749–759 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

