Differential impact of L-arginine deprivation on the activation and effector functions of T cells and macrophages
- PMID: 19008294
- PMCID: PMC2642643
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0508310
Differential impact of L-arginine deprivation on the activation and effector functions of T cells and macrophages
Abstract
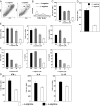
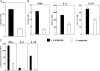
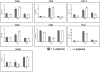
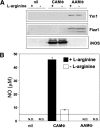
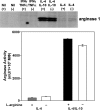
The metabolism of the amino acid L-arginine is emerging as a crucial mechanism for the regulation of immune responses. Here, we characterized the impact of L-arginine deprivation on T cell and macrophage (MPhi) effector functions: We show that whereas L-arginine is required unconditionally for T cell activation, MPhi can up-regulate activation markers and produce cytokines and chemokines in the absence of L-arginine. Furthermore, we show that L-arginine deprivation does not affect the capacity of activated MPhi to up-regulate L-arginine-metabolizing enzymes such as inducible NO synthase and arginase 1. Thus, our results show that to exert their effector functions, T cells and MPhi have different requirements for L-arginine.
Figures
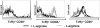
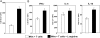
References
-
- Popovic P J, Zeh H J, III, Ochoa J B. Arginine and immunity. J Nutr. 2007;137:1681S–1686S. - PubMed
-
- Morris S M., Jr Arginine metabolism: boundaries of our knowledge. J Nutr. 2007;137:1602S–1609S. - PubMed
-
- Munder M, Eichmann K, Moran J M, Centeno F, Soler G, Modolell M. Th1/Th2-regulated expression of arginase isoforms in murine macrophages and dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1999;163:3771–3777. - PubMed
-
- Jost MM, Ninci E, Meder B, Kempf C, van Royen N, Hua J, Berger B, Hoefer I, Modolell M, Buschmann I. Divergent effects of GM-CSF and TGF-(1 on bone marrow-derived macrophage arginase-1 activity, MCP-1 expresssion and matrix-metalloproteinase-12: a potential role during arteriogenesis. FASEB J. 2003;17:2281–2283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

