The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor regulates endogenous glucose production and muscle glucose uptake independent of its incretin action
- PMID: 19008308
- PMCID: PMC2654733
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-0945
The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor regulates endogenous glucose production and muscle glucose uptake independent of its incretin action
Abstract
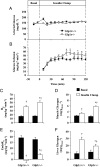
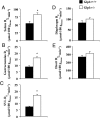
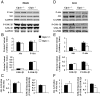
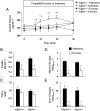
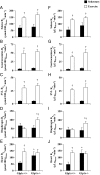
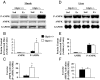
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) diminishes postmeal glucose excursions by enhancing insulin secretion via activation of the beta-cell GLP-1 receptor (Glp1r). GLP-1 may also control glucose levels through mechanisms that are independent of this incretin effect. The hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp (insulin clamp) and exercise were used to examine the incretin-independent glucoregulatory properties of the Glp1r because both perturbations stimulate glucose flux independent of insulin secretion. Chow-fed mice with a functional disruption of the Glp1r (Glp1r(-/-)) were compared with wild-type littermates (Glp1r(+/+)). Studies were performed on 5-h-fasted mice implanted with arterial and venous catheters for sampling and infusions, respectively. During insulin clamps, [3-(3)H]glucose and 2[(14)C]deoxyglucose were used to determine whole-body glucose turnover and glucose metabolic index (R(g)), an indicator of glucose uptake. R(g) in sedentary and treadmill exercised mice was determined using 2[(3)H]deoxyglucose. Glp1r(-/-) mice exhibited increased glucose disappearance, muscle R(g), and muscle glycogen levels during insulin clamps. This was not associated with enhanced muscle insulin signaling. Glp1r(-/-) mice exhibited impaired suppression of endogenous glucose production and hepatic glycogen accumulation during insulin clamps. This was associated with impaired liver insulin signaling. Glp1r(-/-) mice became significantly hyperglycemic during exercise. Muscle R(g) was normal in exercised Glp1r(-/-) mice, suggesting that hyperglycemia resulted from an added drive to stimulate glucose production. Muscle AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation was higher in exercised Glp1r(-/-) mice. This was associated with increased relative exercise intensity and decreased exercise endurance. In conclusion, these results show that the endogenous Glp1r regulates hepatic and muscle glucose flux independent of its ability to enhance insulin secretion.
Figures
References
-
- McIntyre N, Holdsworth CD, Turner DS 1964 New interpretation of oral glucose tolerance. Lancet 2:20–21 - PubMed
-
- Dupre J, Ross SA, Watson D, Brown JC 1973 Stimulation of insulin secretion by gastric inhibitory polypeptide in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 37:826–828 - PubMed
-
- Kreymann B, Williams G, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR 1987 Glucagon-like peptide-1 7–36: a physiological incretin in man. Lancet 2:1300–1304 - PubMed
-
- Campos RV, Lee YC, Drucker DJ 1994 Divergent tissue-specific and developmental expression of receptors for glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 in the mouse. Endocrinology 134:2156–2164 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

