d,l-Sotalol at therapeutic concentrations facilitates the occurrence of long-lasting non-stationary reentry during ventricular fibrillation in isolated rabbit hearts
- PMID: 19008631
- PMCID: PMC3060151
- DOI: 10.1253/circj.cj-08-0540
d,l-Sotalol at therapeutic concentrations facilitates the occurrence of long-lasting non-stationary reentry during ventricular fibrillation in isolated rabbit hearts
Abstract
Background: The effects of d,l-sotalol at therapeutic concentrations (<or=10 mg/L) on wavefront dynamics during ventricular fibrillation (VF) and electrophysiological heterogeneity remain unclear.
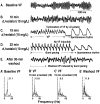
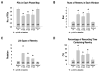
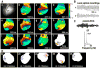
Methods and results: By using an optical mapping system, epicardial activation patterns of VF were studied in 6 Langendorff-perfused rabbit hearts at baseline, during 10 mg/L d,l-sotalol infusion, and after washout. In an additional 4 hearts, action potential duration (APD), conduction velocity, and wavelength (WL) restitutions were determined. During d,l-sotalol infusion, VF was terminated in 3 of the 6 hearts. Only 1 heart developed transient ventricular tachycardia (VT). d,l-Sotalol reduced the number of phase singularities (ie, wavebreak) during VF (P<0.05), and it also increased the occurrence frequency (P<0.05) and lifespan (P<0.05) of epicardial reentry during VF. These reentries were non-stationary in nature and did not anchor on anatomical structures. Restitution data showed that d,l-sotalol flattened APD restitution. Furthermore, APD dispersion and spatial heterogeneity of restitutions were not enhanced by d,l-sotalol.
Conclusions: d,l-Sotalol at therapeutic concentrations decreased wavebreak and facilitated the occurrence of long-lasting, non-stationary reentry during VF. However, VT rarely occurred. The related mechanisms include: (1) flattening of APD restitution without enhancement of spatial heterogeneity of electrophysiological properties, causing wavefront organization, and (2) WL prolongation, preventing steady anchoring of reentry.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- Mason JW. A comparison of electrophysiologic testing with Holter monitoring to predict antiarrhythmic-drug efficacy for ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Electrophysiologic Study versus Electrocardiographic Monitoring Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:445–51. - PubMed
-
- Mason JW. A comparison of seven antiarrhythmic drugs in patients with ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Electrophysiologic Study versus Electrocardiographic Monitoring Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:452–8. - PubMed
-
- Chorro FJ, Canoves J, Guerrero J, Mainar L, Sanchis J, Such L, et al. Alteration of ventricular fibrillation by flecainide, verapamil, and sotalol: an experimental study. Circulation. 2000;101:1606–15. - PubMed
-
- Pak HN, Kim YH, Hwang GS, Lee SJ, Lee HS, Lim HE, et al. Antifibrillatory and Proarrhythmic Effects of d,l-Sotalol Mediated by the Action Potential Duration Restitution Kinetics. Korean Circulation J. 2005;35:282–289.
-
- Wu TJ, Lin SF, Weiss JN, Ting CT, Chen PS. Two types of ventricular fibrillation in isolated rabbit hearts: importance of excitability and action potential duration restitution. Circulation. 2002;106:1859–66. - PubMed

