Molecular basis for G-actin binding to RPEL motifs from the serum response factor coactivator MAL
- PMID: 19008859
- PMCID: PMC2583105
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.235
Molecular basis for G-actin binding to RPEL motifs from the serum response factor coactivator MAL
Abstract
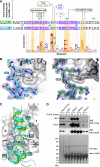
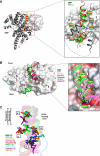
Serum response factor transcriptional activity is controlled through interactions with regulatory cofactors such as the coactivator MAL/MRTF-A (myocardin-related transcription factor A). MAL is itself regulated in vivo by changes in cellular actin dynamics, which alter its interaction with G-actin. The G-actin-sensing mechanism of MAL/MRTF-A resides in its N-terminal domain, which consists of three tandem RPEL repeats. We describe the first molecular insights into RPEL function obtained from structures of two independent RPEL(MAL) peptide:G-actin complexes. Both RPEL peptides bind to the G-actin hydrophobic cleft and to subdomain 3. These RPEL(MAL):G-actin structures explain the sequence conservation defining the RPEL motif, including the invariant arginine. Characterisation of the RPEL(MAL):G-actin interaction by fluorescence anisotropy and cell reporter-based assays validates the significance of actin-binding residues for proper MAL localisation and regulation in vivo. We identify important differences in G-actin engagement between the two RPEL(MAL) structures. Comparison with other actin-binding proteins reveals an unexpected similarity to the vitamin-D-binding protein, extending the G-actin-binding protein repertoire.
Figures



References
-
- Bubb MR, Govindasamy L, Yarmola EG, Vorobiev SM, Almo SC, Somasundaram T, Chapman MS, Agbandje-McKenna M, McKenna R (2002) Polylysine induces an antiparallel actin dimer that nucleates filament assembly: crystal structure at 3.5-Å resolution. J Biol Chem 277: 20999–21006 - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (Collaborative Computational Project N) (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 50: 760–763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

