Transcriptional regulation by AIRE: molecular mechanisms of central tolerance
- PMID: 19008896
- PMCID: PMC2785478
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2450
Transcriptional regulation by AIRE: molecular mechanisms of central tolerance
Abstract
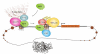
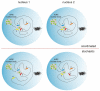
The negative selection of T cells in the thymus is necessary for the maintenance of self tolerance. Medullary thymic epithelial cells have a key function in this process as they express a large number of tissue-specific self antigens that are presented to developing T cells. Mutations in the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) protein cause a breakdown of central tolerance that is associated with decreased expression of self antigens in the thymus. In this Review, we discuss the role of AIRE in the thymus and recent advances in our understanding of how AIRE might function at the molecular level to regulate gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Takahama Y. Journey through the thymus: stromal guides for T-cell development and selection. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:127–35. - PubMed
-
- Anderson G, Lane PJ, Jenkinson EJ. Generating intrathymic microenvironments to establish T-cell tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:954–63. - PubMed
-
- Kyewski B, Klein L. A central role for central tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:571–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

