Neurophysiology of swallowing: effects of age and bolus type
- PMID: 19010424
- PMCID: PMC2630466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.012
Neurophysiology of swallowing: effects of age and bolus type
Abstract
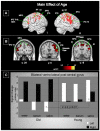
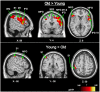
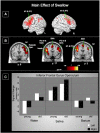
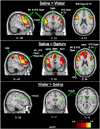
This study examined age-related changes in swallowing from an integrated biomechanical and functional imaging perspective in order to more comprehensively characterize changes in swallowing associated with age. We examined swallowing-related fMRI brain activity and videoflouroscopic biomechanics of three bolus types (saliva, water and barium) in 12 young and 11 older adults. We found that age-related neurophysiological changes in swallowing are evident. The group of older adults recruited more cortical regions than young adults, including the pericentral gyri and inferior frontal gyrus pars opercularis and pars triangularis (primarily right-sided). Saliva swallows elicited significantly higher BOLD responses in regions important for swallowing compared to water and barium. In separate videofluoroscopy sessions, we obtained durational measures of supine swallowing. The older cohort had significantly longer delays before the onset of the pharyngeal swallow response and increased residue of ingested material in the pharynx. These findings suggest that older adults without neurological insult elicit more cortical involvement to complete the same swallowing tasks as younger adults.
Figures

References
-
- Butti M, Pastori A, Merzagora A, Zucca C, Bianchi A, Reni G, et al. Multimodal analysis of a sustained attention protocol: continuous performance test assessed with near infrared spectroscopy and EEG. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2006;1:1040–1043. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun KH, Gibson B, Hartley L, Minton J, Hokanson JA. Age-related changes in oral sensation. Laryngoscope. 1992;102:109–116. - PubMed
-
- Cerf-Ducastel B, Van de Moortele PF, MacLeod P, Le Bihan D, Faurion A. Interaction of gustatory and lingual somatosensory perceptions at the cortical level in the human: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Chem. Senses. 2001;26:371–383. - PubMed
-
- Daniels SK, Foundas AL. The role of the insular cortex in dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1997;12:146–156. - PubMed
-
- Dejaeger E, Pelemans W, Ponette E, Vantrappen G. Effect of body position on deglutition. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1994;39:762–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

