Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor blockade improves outcome in mouse model of lung injury
- PMID: 19011156
- PMCID: PMC2633054
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200802-228OC
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor blockade improves outcome in mouse model of lung injury
Abstract
Rationale: The insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) pathway is an important determinant of survival and proliferation in many cells. However, little is known about the role of the IGF-I pathway in lung injury. We previously showed elevated levels of IGF-I in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Furthermore, immunodepletion of IGF from acute respiratory distress syndrome bronchoalveolar lavage increased fibroblast apoptosis.
Objectives: We examined the effect of blockade of type 1 IGF tyrosine kinase receptor (IGF-IR) in a murine model of bleomycin-induced lung injury and fibrosis.
Methods: Mice were treated with a monoclonal antibody against the IGF-I receptor (A12) or vehicle after intratracheal bleomycin instillation.
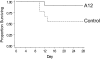
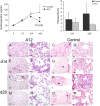
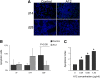
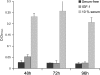
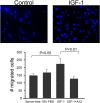
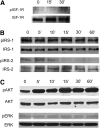
Measurements and main results: Mice treated with A12 antibody had significantly improved survival after bleomycin injury compared with control mice. Both groups of mice had a similar degree of fibrosis on days 7 and 14, but by Day 28 the A12-treated group had significantly less fibrosis. Delayed treatment with A12 also resulted in decreased fibrosis. A12-treated mice had significantly decreased apoptotic cells on Day 28 compared with control mice. We confirmed that A12 treatment induced mouse lung fibroblast apoptosis in vitro. In addition, IGF-I increased lung fibroblast migration. The primary pathway activated by IGF-I in lung fibroblasts was the insulin receptor substrate-2/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt axis.
Conclusions: IGF-I regulated survival and migration of fibrogenic cells in the lung. Blockade of the IGF pathway increased fibroblast apoptosis and subsequent resolution of pulmonary fibrosis. Thus, IGF-IR may be a potential target for treatment of lung injury and fibrosis.
Figures


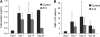

References
-
- LeRoith D, Roberts CT Jr. The insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett 2003;195:127–137. - PubMed
-
- Kurmasheva RT, Houghton PJ. IGF-I mediated survival pathways in normal and malignant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006;1766:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Maeda A, Hiyama K, Yamakido H, Ishioka S, Yamakido M. Increased expression of platelet-derived growth factor A and insulin-like growth factor-I in BAL cells during the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Chest 1996;109:780–786. - PubMed
-
- Krein PM, Sabatini PJ, Tinmouth W, Green FH, Winston BW. Localization of insulin-like growth factor-I in lung tissues of patients with fibroproliferative acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003;167:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

