Treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain by uncoupling Src from the NMDA receptor complex
- PMID: 19011637
- PMCID: PMC3616027
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1883
Treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain by uncoupling Src from the NMDA receptor complex
Abstract
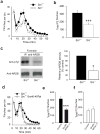
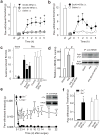
Chronic pain hypersensitivity depends on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). However, clinical use of NMDAR blockers is limited by side effects resulting from suppression of the physiological functions of these receptors. Here we report a means to suppress pain hypersensitivity without blocking NMDARs, but rather by inhibiting the binding of a key enhancer of NMDAR function, the protein tyrosine kinase Src. We show that a peptide consisting of amino acids 40-49 of Src fused to the protein transduction domain of the HIV Tat protein (Src40-49Tat) prevented pain behaviors induced by intraplantar formalin and reversed pain hypersensitivity produced by intraplantar injection of complete Freund's adjuvant or by peripheral nerve injury. Src40-49Tat had no effect on basal sensory thresholds, acute nociceptive responses or cardiovascular, respiratory, locomotor or cognitive functions. Thus, through targeting of Src-mediated enhancement of NMDARs, inflammatory and neuropathic pain are suppressed without the deleterious consequences of directly blocking NMDARs, an approach that may be of broad relevance to managing chronic pain.
Figures




Comment in
-
Breaking the pain connection.Nat Med. 2008 Dec;14(12):1313-5. doi: 10.1038/nm1208-1313. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 19057553 No abstract available.
-
Uncoupling Src from the NMDA receptor treats chronic pain in rodents.Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2009 Mar;5(3):121. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2009. PMID: 20408267 No abstract available.
References
-
- Woolf CJ, Salter MW. Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science. 2000;288:1765–1769. - PubMed
-
- Ji RR, Strichartz G. Cell signaling and the genesis of neuropathic pain. Sci STKE. 2004;2004:reE14. - PubMed
-
- Julius D, Basbaum AI. Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature. 2001;413:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Coull JA, et al. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature. 2005;438:1017–1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

