Peptidase substrates via global peptide profiling
- PMID: 19011639
- PMCID: PMC2730040
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.126
Peptidase substrates via global peptide profiling
Abstract
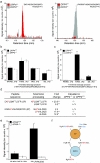
Peptide metabolism is a complex process that involves many proteins working in concert. Mass spectrometry-based global peptide profiling of mice lacking dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) identified endogenous DPP4 substrates and revealed an unrecognized pathway during proline peptide catabolism that interlinks aminopeptidase and DPP4 activities. Together, these studies elucidate specific aspects of DPP4-regulated metabolism and, more generally, highlight the utility of global peptide profiling for studying peptide metabolism in vivo.
Figures
Comment in
-
Metabolomics cuts to the chase to chase the cuts.Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Jan;5(1):5-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0109-5. Nat Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19088710 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Expanding the dipeptidyl peptidase 4-regulated peptidome via an optimized peptidomics platform.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Mar 24;132(11):3819-30. doi: 10.1021/ja909524e. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20178363 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of Porphyromonas gingivalis dipeptidyl peptidase 4 and structure-activity relationships based on inhibitor profiling.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Oct 20;139:482-491. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.024. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28826083
-
Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV as a Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Aug 1;102(8):2930-2940. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00346. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28575350
-
Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of action of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors.Endocr Rev. 2014 Dec;35(6):992-1019. doi: 10.1210/er.2014-1035. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Endocr Rev. 2014. PMID: 25216328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitor therapy in type 2 diabetes: Control of the incretin axis and regulation of postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism.Peptides. 2018 Feb;100:158-164. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.11.023. Peptides. 2018. PMID: 29412815 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitors: A Focus on Microalbuminuria.Int J Endocrinol. 2013;2013:895102. doi: 10.1155/2013/895102. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Int J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 24089613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity-based proteomics of enzyme superfamilies: serine hydrolases as a case study.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 9;285(15):11051-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R109.097600. Epub 2010 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20147750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic strategies for the identification of new enzyme functions and metabolic pathways.EMBO Rep. 2014 Jun;15(6):657-69. doi: 10.15252/embr.201338283. Epub 2014 May 14. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 24829223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome inhibitors alter levels of intracellular peptides in HEK293T and SH-SY5Y cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 31;9(7):e103604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103604. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25079948 Free PMC article.
-
How chemoproteomics can enable drug discovery and development.Chem Biol. 2012 Jan 27;19(1):11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.01.001. Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22284350 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

