Exceeding the limits of liver histology markers
- PMID: 19012989
- PMCID: PMC2637134
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.07.039
Exceeding the limits of liver histology markers
Abstract
Background/aims: Alternatives to liver biopsy for staging liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV) have not appeared accurate enough for widespread clinical use. We characterized the magnitude of the impact of error in the "gold standard" on the observed diagnostic accuracy of surrogate markers.
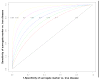
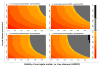
Methods: We calculated the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) for a surrogate marker against the gold standard (biopsy) for a range of possible performances of each test (biopsy and marker) against truth and a gradient of clinically significant disease prevalence.
Results: In the 'best' scenario where liver biopsy accuracy is highest (sensitivity and specificity of biopsy are 90%) and the prevalence of significant disease 40%, the calculated AUROC would be 0.90 for a perfect marker (99% actual accuracy) which is within the range of what has already been observed. With lower biopsy sensitivity and specificity, AUROC determinations > 0.90 could not be achieved even for a marker that perfectly measured disease.
Conclusions: We demonstrate that error in the liver biopsy result itself makes it impossible to distinguish a perfect surrogate from ones that are now judged by some as clinically unacceptable. An alternative gold standard is needed to assess the accuracy of tests used to stage HCV-related liver disease.
Figures
Comment in
-
Liver biopsy: the best, not the gold standard.J Hepatol. 2009 Jan;50(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.10.014. Epub 2008 Nov 6. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19017551 No abstract available.
-
What is the actual role of diagnosis and how to assess it?J Hepatol. 2009 Apr;50(4):828-9; author reply 829-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.012. Epub 2009 Jan 9. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19231007 No abstract available.
-
Liver biopsy: the best standard...when everything else fails.J Hepatol. 2009 Jun;50(6):1267-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.02.010. Epub 2009 Mar 12. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19380171 No abstract available.
References
-
- Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2004;39:1147–1171. - PubMed
-
- Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update of recommendations. Hepatology. 2004;39:857–861. - PubMed
-
- J Hepatol; Proceedings of the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) International Consensus Conference on Hepatitis B; September 14-16, 2002; Geneva, Switzerland. 2003. pp. S1–S235. - PubMed
-
- Poynard T, Ratziu V, Bedossa P. Appropriateness of liver biopsy. Can J Gastroenterol. 2000;14:543–548. - PubMed
-
- Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S. Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:495–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

