A translational profiling approach for the molecular characterization of CNS cell types
- PMID: 19013281
- PMCID: PMC2696821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.028
A translational profiling approach for the molecular characterization of CNS cell types
Abstract
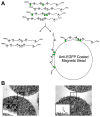
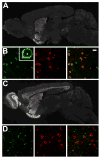
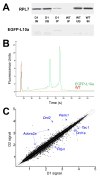
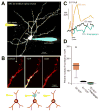
The cellular heterogeneity of the brain confounds efforts to elucidate the biological properties of distinct neuronal populations. Using bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) transgenic mice that express EGFP-tagged ribosomal protein L10a in defined cell populations, we have developed a methodology for affinity purification of polysomal mRNAs from genetically defined cell populations in the brain. The utility of this approach is illustrated by the comparative analysis of four types of neurons, revealing hundreds of genes that distinguish these four cell populations. We find that even two morphologically indistinguishable, intermixed subclasses of medium spiny neurons display vastly different translational profiles and present examples of the physiological significance of such differences. This genetically targeted translating ribosome affinity purification (TRAP) methodology is a generalizable method useful for the identification of molecular changes in any genetically defined cell type in response to genetic alterations, disease, or pharmacological perturbations.
Figures


Comment in
-
Unlocking CNS cell type heterogeneity.Cell. 2008 Nov 14;135(4):596-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.031. Cell. 2008. PMID: 19013270
References
-
- Brakeman PR, Lanahan AA, O’Brien R, Roche K, Barnes CA, Huganir RL, Worley PF. Homer: a protein that selectively binds metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature. 1997;386:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Day M, Wang Z, Ding J, An X, Ingham CA, Shering AF, Wokosin D, Ilijic E, Sun Z, Sampson AR, et al. Selective elimination of glutamatergic synapses on striatopallidal neurons in Parkinson disease models. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:251–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 NS034696/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH074866/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5F32DA021487/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG009464/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH074866/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DA021487/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA10044/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 5UL1RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS34696/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA010044/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034696/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG09464/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

