Time-dependent adaptation in the hemodynamic response to hypoxia
- PMID: 19013546
- PMCID: PMC2662762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2008.10.013
Time-dependent adaptation in the hemodynamic response to hypoxia
Abstract
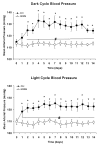
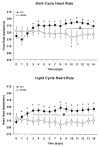
In rats, acute exposure to hypoxia causes a decrease in mean arterial pressure (MAP) caused by a predominance of hypoxic vasodilation over chemoreflex-induced vasoconstriction. We previously demonstrated that exposure to chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) impairs hypoxic vasodilation in isolated resistance arteries; therefore, we hypothesized that the acute systemic hemodynamic responses to hypoxia would be altered by exposure to CIH. To test this hypothesis, rats were exposed to CIH for 14 days. Heart rate (HR) and MAP were monitored by telemetry. On the first day of CIH exposure, acute episodes of hypoxia caused a decrease in MAP (-9+/-5 mmHg) and an increase in HR (+45+/-4 beats/min). On the 14th day of CIH exposure the depressor response was attenuated (-4+/-1mmHg; 44% of the day 1 response) and the tachycardia was enhanced (+68+/-2 beats/min; 151% of the day 1 response). The observed time-dependent modulation of the acute hemodynamic responses to hypoxia may reflect important changes in neurocirculatory regulation that contribute to CIH-induced hypertension.
Figures

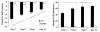
Similar articles
-
Altered sympathetic reflexes and vascular reactivity in rats after exposure to chronic intermittent hypoxia.J Physiol. 2011 Mar 15;589(Pt 6):1463-76. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.200691. Epub 2011 Jan 17. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21242253 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathetic response to chemostimulation in conscious rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009 Apr 30;166(2):102-6. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2009.02.010. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19429526
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia increases blood pressure and expression of FosB/DeltaFosB in central autonomic regions.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):R131-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00830.2010. Epub 2011 May 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21543638 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular and ventilatory acclimatization induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia: a role for the carotid body in the pathophysiology of sleep apnea.Biol Res. 2005;38(4):335-40. doi: 10.4067/s0716-97602005000400004. Biol Res. 2005. PMID: 16579514 Review.
-
Sex differences in the respiratory-sympathetic coupling in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;256:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28893610 Review.
Cited by
-
Perinatal intermittent hypoxia increases early susceptibility to ANG II-induced hypertension in adult male but not in female Sprague-Dawley rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 May 1;324(5):F483-F493. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00308.2022. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36951371 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia promotes glomerular hyperfiltration and potentiates hypoxia-evoked decreases in renal perfusion and PO2.Front Physiol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1235289. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1235289. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37485067 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying hypoxia-induced chemoreceptor sensitivity in the awake rodent.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Oct 1;117(7):816-24. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00484.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 31. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 25080926 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide and miR21 are suitable biomarkers of hypoxic exposure.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Dec 1;323(6):R900-R909. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00199.2022. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36250874 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of allergic airway inflammation and chronic intermittent hypoxia on systemic blood pressure.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):R566-R574. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00325.2019. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32903041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barros RC, Bonagamba LG, Okamoto-Canesin R, de OM, Branco LG, Machado BH. Cardiovascular responses to chemoreflex activation with potassium cyanide or hypoxic hypoxia in awake rats. Auton Neurosci. 2002;97:110–115. - PubMed
-
- Behm R, Mewes H, Muinck Keizer WH, Unger T, Rettig R. Cardiovascular and renal effects of hypoxia in conscious carotid body-denervated rats. J Appl Physiol. 1993;74:2795–2800. - PubMed
-
- Biesold D, Kurosawa M, Sato A, Trzebski A. Hypoxia and hypercapnia increase the sympathoadrenal medullary functions in anesthetized, artificially ventilated rats. Jpn J Physiol. 1989;39:511–522. - PubMed
-
- Campen MJ, Shimoda LA, O'Donnell CP. Acute and chronic cardiovascular effects of intermittent hypoxia in C57BL/6J mice. J Appl Physiol. 2005;99:2028–2035. - PubMed
-
- Cuspidi C, Macca G, Sampieri L, Fusi V, Severgnini B, Michev I, Salerno M, Magrini F, Zanchetti A. Target organ damage and non-dipping pattern defined by two sessions of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in recently diagnosed essential hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. 2001;19:1539–1545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

