Chronic reductions in serotonin transporter function prevent 5-HT1B-induced behavioral effects in mice
- PMID: 19013555
- PMCID: PMC2674010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.09.026
Chronic reductions in serotonin transporter function prevent 5-HT1B-induced behavioral effects in mice
Abstract
Background: Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is characterized by intrusive thoughts, images, or impulses and/or repetitive stereotypical behavior. Obsessive-compulsive disorder patients exhibit reduced prepulse inhibition (PPI) and symptom exacerbation after challenge with 5-HT1B receptor agonists. Recently, gain-of-function alleles of the serotonin transporter (5-HTT) have been associated with OCD. We tested the hypothesis that reducing 5-HTT function chronically, either genetically or via serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) treatment, attenuates PPI deficits and perseverative hyperlocomotion induced by 5-HT1B agonists in mice.
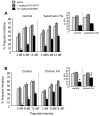
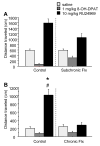
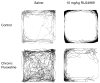
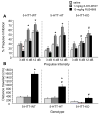
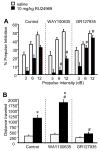
Methods: Mice received subchronic or chronic pretreatment with the SRI fluoxetine and acute treatment with RU24969 (5-HT1A/1B agonist) or 8-OH-DPAT (5-HT1A agonist) and were assessed for PPI, locomotor activity, and spatial patterns of locomotion. The same measures were evaluated in 5-HTT wild-type (WT), heterozygous (HT), and knockout (KO) mice after RU24969 treatment. The effects of WAY100635 (5-HTA antagonist) or GR127935 (5-HT1B/D antagonist) pretreatment on RU24969-induced effects were evaluated. Finally, 5-HT1B binding and functional coupling were assessed in 5-HTT-WT, -HT, and -KO mice, and normal fluoxetine-treated mice.
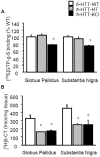
Results: Chronic, but not subchronic, fluoxetine treatment prevented RU24969-induced PPI deficits and perseverative hyperlocomotion. These RU24969-induced effects were mediated via 5-HT1B and not 5-HT1A receptors. 5-HTT-KO mice showed no effects of RU24969, and 5-HTT-HT mice exhibited intermediate phenotypes. 5-HT1B binding and functional coupling were reduced in the globus pallidus and substantia nigra of 5-HTT-KO mice.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that chronic, but not subchronic, fluoxetine treatment and 5-HTT knockout robustly attenuate 5-HT1B agonist-induced PPI deficits and perseverative hyperlocomotion. These results may have implications for the etiology and treatment of OCD.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure/Conflict of Interest
S.C. Dulawa, K.A. Holick, N.A. Shanahan, V. Masten, M. Ansorge, C. Waeber, and J.A. Gingrich reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. M.A. Geyer holds an equity interest in San Diego Instruments. R. Hen receives compensation as a consultant for BrainCells, Inc., PsychoGenics, Inc., Memory Pharmaceuticals, Roche, Astra Zeneca, and Lundbeck in relation to the generation of novel antidepressants.
Figures
References
-
- Sanders AR, Duan J, Gejman PV. DNA variation and psychopharmacology of the human serotonin receptor 1B (HTR1B) gene. Pharmacogenomics. 2002;3:745–762. - PubMed
-
- Mundo E, Richter MA, Sam F, Macciardi F, Kennedy JL. Is the 5- HT(1Dbeta) receptor gene implicated in the pathogenesis of obsessive-compulsive disorder? Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1160–1161. - PubMed
-
- Stein DJ, Van Heerden B, Wessels CJ, Van Kradenburg J, Warwick J, Wasserman HJ. Single photon emission computed tomography of the brain with Tc-99m HMPAO during sumatriptan challenge in obsessive-compulsive disorder: investigating the functional role of the serotonin auto-receptor. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1999;23:1079–1099. - PubMed
-
- Gross-Isseroff R, Cohen R, Sasson Y, Voet H, Zohar J. Serotonergic dissection of obsessive compulsive symptoms: a challenge study with m-chlorophenylpiperazine and sumatriptan. Neuropsychobiology. 2004;50:200–205. - PubMed
-
- Koran LM, Pallanti S, Quercioli L. Sumatriptan, 5-HT(1D) receptors and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2001;11:169–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH079424/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH071555/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA02925/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS049263/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS052195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01MH071555/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32DA07255-15/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS052195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007255/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS049263/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH079424/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA002925/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

