Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in the brain: properties and future directions
- PMID: 19014390
- PMCID: PMC2667944
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05723.x
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in the brain: properties and future directions
Abstract
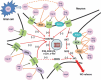
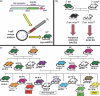
Angiotensin (Ang)-converting enzyme (ACE) 2 cleaves Ang-II into the vasodilator peptide Ang-(1-7), thus acting as a pivotal element in balancing the local effects of these peptides. ACE2 has been identified in various tissues and is supposed to be a modulator of cardiovascular function. Decreases in ACE2 expression and activity have been reported in models of hypertension, heart failure, atherosclerosis, diabetic nephropathy and others. In addition, the expression level and/or activity are affected by other renin-angiotensin system components (e.g., ACE and AT1 receptors). Local inhibition or global deletion of brain ACE2 induces a reduction in baroreflex sensitivity. Moreover, ACE2-null mice have been shown to exhibit either blood pressure or cardiac dysfunction phenotypes. On the other hand, over-expression of ACE2 exerts protective effects in local tissues, including the brain. In this review, we will first summarize the major findings linking ACE2 to cardiovascular function in the periphery then focus on recent discoveries related to ACE2 in the CNS. Finally, we will unveil new tools designed to address the importance of central ACE2 in various diseases, and discuss the potential for this carboxypeptidase as a new target in the treatment of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: central regulator for cardiovascular function.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2010 Jun;12(3):170-5. doi: 10.1007/s11906-010-0105-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2010. PMID: 20424953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACE2 and vasoactive peptides: novel players in cardiovascular/renal remodeling and hypertension.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):217-37. doi: 10.1177/1753944715597623. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26275770 Review.
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated reduction of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity in the brain impairs baroreflex function in hypertensive mice.Hypertension. 2009 Feb;53(2):210-6. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.123844. Epub 2009 Jan 5. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19124678 Free PMC article.
-
The two fACEs of the tissue renin-angiotensin systems: implication in cardiovascular diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(12):1231-45. doi: 10.2174/138161207780618911. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17504232 Review.
-
Role of ACE2 in diastolic and systolic heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2012 Sep;17(4-5):683-91. doi: 10.1007/s10741-011-9259-x. Heart Fail Rev. 2012. PMID: 21638102 Review.
Cited by
-
The COVID-19 pandemic and Alzheimer's disease: mutual risks and mechanisms.Transl Neurodegener. 2022 Sep 11;11(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00316-y. Transl Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 36089575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Endothelial Dysfunction after COVID-19 Infection Shown by Transcranial Color-Coded Doppler: A Cross-Sectional Study.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 13;10(10):2550. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102550. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289812 Free PMC article.
-
Can Infection of COVID-19 Virus Exacerbate Alzheimer's Symptoms? Hypothetic Possible Role of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2/Mas/ Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Axis and Tau Hyper-phosphorylation.Adv Biomed Res. 2020 Aug 28;9:36. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_72_20. eCollection 2020. Adv Biomed Res. 2020. PMID: 33072648 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: The old door for new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.Rev Med Virol. 2020 Sep;30(5):e2122. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2122. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Rev Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32602627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns of COVID-19-related headache: A cross-sectional study.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022 Aug;219:107339. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107339. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35753162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambuhl P., Gyurko R. and Phillips M. I. (1995) A decrease in angiotensin receptor binding in rat brain nuclei by antisense oligonucleotides to the angiotensin AT1 receptor. Regul. Pept. 59, 171–182. - PubMed
-
- Becker L. K., Santos R. A. S. and Campagnole‐Santos M. J. (2005) Cardiovascular effects of angiotensin II and angiotensin‐(1–7) at the RVLM of trained normotensive rats. Brain Res. 1040, 121–128. - PubMed
-
- Becker L. K., Etelvino G. M., Walther T., Santos R. A. S. and Campagnole‐Santos M. J. (2007) Immunofluorescence localization of the receptor Mas in cardiovascular‐related areas of the rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 293, H1416–H1424. - PubMed
-
- Blume A., Herdegen T. and Unger T. (1999) Angiotensin peptides and inducible transcription factors. J. Mol. Med. 77, 339–357. - PubMed
-
- Bomtempo C. A., Santos G. F., Santos R. A. and Campagnole‐Santos M. J. (1998) Interaction of bradykinin and angiotensin‐(1–7) in the central modulation of the baroreflex control of the heart rate. J. Hypertens. 16, 1797–1804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

