Giant breast tumors: surgical management of phyllodes tumors, potential for reconstructive surgery and a review of literature
- PMID: 19014438
- PMCID: PMC2648962
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-6-117
Giant breast tumors: surgical management of phyllodes tumors, potential for reconstructive surgery and a review of literature
Abstract
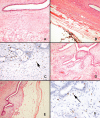
Background: Phyllodes tumors are biphasic fibroepithelial neoplasms of the breast. While the surgical management of these relatively uncommon tumors has been addressed in the literature, few reports have commented on the surgical approach to tumors greater than ten centimeters in diameter - the giant phyllodes tumor.
Case presentation: We report two cases of giant breast tumors and discuss the techniques utilized for pre-operative diagnosis, tumor removal, and breast reconstruction. A review of the literature on the surgical management of phyllodes tumors was performed.
Conclusion: Management of the giant phyllodes tumor presents the surgeon with unique challenges. The majority of these tumors can be managed by simple mastectomy. Axillary lymph node metastasis is rare, and dissection should be limited to patients with pathologic evidence of tumor in the lymph nodes.
Figures



References
-
- Noguchi S, Motomura K, Inaji H, Imaoka S, Koyama H. Clonal analysis of fibroadenoma and phyllodes tumor of the breast. Cancer Res. 1993;53:4071–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

