Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits influenza virus neuraminidase
- PMID: 19014974
- PMCID: PMC7114187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.10.006
Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits influenza virus neuraminidase
Abstract
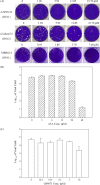
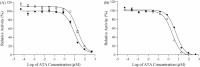
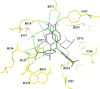
There is a continuing threat that the highly pathogenic avian influenza virus will cause future influenza pandemics. In this study, we screened a library of compounds that are biologically active and structurally diverse for inhibitory activity against influenza neuraminidase (NA). We found that aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) is a potent inhibitor of NA activity of both group-1 and group-2 influenza viruses with IC(50)s (effective concentration to inhibit NA activity by 50%) values at low micromolar concentrations. ATA was equally potent in inhibiting the NA activity derived from wild-type NA and its H274Y mutant which renders NA resistance to inhibition by oseltamivir. Although ATA is structurally distinct from sialic acid, molecular modeling experiments suggested that ATA binds to NA at the enzyme's substrate binding site. These results indicate that ATA may be a good starting material for the design of a novel class of NA inhibitors for the treatment influenza viruses.
Figures


References
-
- Abed Y., Baz M., Boivin G. Impact of neuraminidase mutations conferring influenza resistance to neuraminidase inhibitors in the N1 and N2 genetic backgrounds. Antiviral Ther. 2006;11:971–976. - PubMed
-
- Andrew D.J., Hay A.W., Evans S.W. Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits apoptosis and supports proliferation in a haemopoietic growth-factor dependent myeloid cell line. Immunopharmacology. 1999;41:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Balzarini J., Mitsuya H., De Clercq E., Broder S. Aurintricarboxylic acid and Evans Blue represent two different classes of anionic compounds which selectively inhibit the cytopathogenicity of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986;136:64–71. - PubMed
-
- Baz M., Abed Y., Boivin G. Characterization of drug-resistant recombinant influenza A/H1N1 viruses selected in vitro with peramivir and zanamivir. Antiviral Res. 2007;74:159–162. - PubMed
-
- Beery R., Haimsohn M., Wertheim N., Hemi R., Nir U., Karasik A., Kanety H., Geier A. Activation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling pathway by the antiapoptotic agents aurintricarboxylic acid and evans blue. Endocrinology. 2001;142:3098–3107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

