Association of serum bicarbonate levels with mortality in patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD
- PMID: 19015169
- PMCID: PMC2721428
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfn633
Association of serum bicarbonate levels with mortality in patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD
Abstract
Background: Metabolic acidosis, usually manifested by low serum bicarbonate level, is common in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and appears to be associated with higher mortality in dialysis patients. It is not known whether a similar association is present in patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD (NDD-CKD).
Methods: We used multivariable-adjusted Cox models to examine the association between baseline and time-variable serum bicarbonate (measured as total CO2) with the outcomes of all-cause mortality and the composite of pre-dialysis mortality or end-stage renal disease in 1240 male patients with moderate and advanced NDD-CKD.
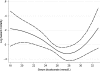
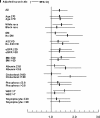
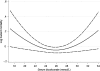
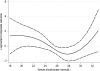
Results: Serum bicarbonate showed a significant U-shaped association with all-cause mortality, with the highest mortality rate observed in patients with baseline serum bicarbonate levels <22 mmol/L [multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) for patients with serum bicarbonate <22 mmol/L versus > or =22 mmol/L: 1.33 (1.05-1.69), P = 0.02] and the lowest mortality observed in patients with baseline serum bicarbonate of 26-29 mmol/L. The associations between lower serum bicarbonate level and mortality were more accentuated in subgroups of patients with better nutritional status and lower inflammation.
Conclusions: Both lower and higher serum bicarbonates are associated with increased all-cause mortality in patients with moderate and advanced NDD-CKD. Clinical trials are needed to determine if therapeutic interventions aimed at optimizing serum bicarbonate can result in improved outcomes in this population.
Figures
References
-
- Kopple JD, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Mehrotra R. Risks of chronic metabolic acidosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005:S21–S27. - PubMed
-
- Kraut JA, Kurtz I. Metabolic acidosis of CKD: diagnosis, clinical characteristics, and treatment. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45:978–993. - PubMed
-
- Franch HA, Mitch WE. Catabolism in uremia: the impact of metabolic acidosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:S78–S81. - PubMed
-
- Bommer J, Locatelli F, Satayathum S, et al. Association of predialysis serum bicarbonate levels with risk of mortality and hospitalization in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS) Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:661–671. - PubMed
-
- Lowrie EG, Lew NL. Death risk in hemodialysis patients: the predictive value of commonly measured variables and an evaluation of death rate differences between facilities. Am J Kidney Dis. 1990;15:458–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

