YAP regulates neural progenitor cell number via the TEA domain transcription factor
- PMID: 19015275
- PMCID: PMC2600760
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1726608
YAP regulates neural progenitor cell number via the TEA domain transcription factor
Abstract
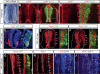
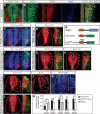
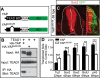
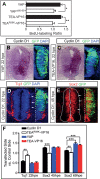
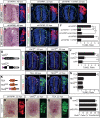
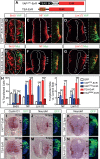
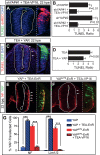
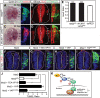
Tight control of cell proliferation is essential for proper growth during development and for tissue homeostasis in mature animals. The evolutionarily conserved Hippo pathway restrains proliferation through a kinase cascade that culminates in the inhibition of the transcriptional coactivator YAP. Unphosphorylated YAP activates genes involved in cell proliferation and survival by interacting with a DNA-binding factor. Here we show that during vertebrate neural tube development, the TEA domain transcription factor (TEAD) is the cognate DNA-binding partner of YAP. YAP and TEAD gain of function causes marked expansion of the neural progenitor population, partly owing to their ability to promote cell cycle progression by inducing cyclin D1 and to inhibit differentiation by suppressing NeuroM. Their loss of function results in increased apoptosis, whereas repressing their target genes leads to premature neuronal differentiation. Inhibiting the upstream kinases of the Hippo pathway also causes neural progenitor overproliferation. Thus, the Hippo pathway plays critical roles in regulating neural progenitor cell number by affecting proliferation, fate choice, and cell survival.
Figures
References
-
- Azakie A., Larkin S.B., Farrance I.K., Grenningloh G., Ordahl C.P. DTEF-1, a novel member of the transcription enhancer factor-1 (TEF-1) multigene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:8260–8265. - PubMed
-
- Bylund M., Andersson E., Novitch B.G., Muhr J. Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1-3 activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2003;6:1162–1168. - PubMed
-
- Camargo F.D., Gokhale S., Johnnidis J.B., Fu D., Bell G.W., Jaenisch R., Brummelkamp T.R. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr. Biol. 2007;17:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Campbell S., Inamdar M., Rodrigues V., Raghavan V., Palazzolo M., Chovnick A. The scalloped gene encodes a novel, evolutionarily conserved transcription factor required for sensory organ differentiation in Drosophila. Genes & Dev. 1992;6:367–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
