Revisiting the mechanism of macrolide-antibiotic resistance mediated by ribosomal protein L22
- PMID: 19015512
- PMCID: PMC2587587
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810357105
Revisiting the mechanism of macrolide-antibiotic resistance mediated by ribosomal protein L22
Abstract
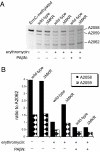
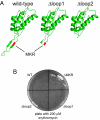
Bacterial antibiotic resistance can occur by many mechanisms. An intriguing class of mutants is resistant to macrolide antibiotics even though these drugs still bind to their targets. For example, a 3-residue deletion (DeltaMKR) in ribosomal protein L22 distorts a loop that forms a constriction in the ribosome exit tunnel, apparently allowing nascent-chain egress and translation in the presence of bound macrolides. Here, however, we demonstrate that DeltaMKR and wild-type ribosomes show comparable macrolide sensitivity in vitro. In Escherichia coli, we find that this mutation reduces antibiotic occupancy of the target site on ribosomes in a manner largely dependent on the AcrAB-TolC efflux system. We propose a model for antibiotic resistance in which DeltaMKR ribosomes alter the translation of specific proteins, possibly via changes in programmed stalling, and modify the cell envelope in a manner that lowers steady-state macrolide levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Roberts MC. Update on macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin, ketolide, and oxazolidinone resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008;282:147–159. - PubMed
-
- Schlünzen F, et al. Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria. Nature. 2001;413:814–821. - PubMed
-
- Tu D, Blaha G, Moore PB, Steitz TA. Structures of MLSBK antibiotics bound to mutated large ribosomal subunits provide a structural explanation for resistance. Cell. 2005;121:257–270. - PubMed
-
- Contreras A, Vázquez D. Cooperative and antagonistic interactions of peptidyl-tRNA and antibiotics with bacterial ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977;74:539–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

