Polarized response of endothelial cells to invasion by Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 19016788
- PMCID: PMC3393649
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01247.x
Polarized response of endothelial cells to invasion by Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
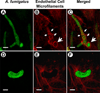
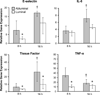
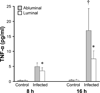
Hyphal invasion of blood vessels is a prominent feature of invasive aspergillosis. During invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae invade the abluminal endothelial cell surface, whereas they invade the luminal endothelial cell surface during haematogenous dissemination. We investigated the endothelial cell response to abluminal and luminal infection with A. fumigatus hyphae in vitro. We found that these hyphae invaded the abluminal endothelial cell surface without inducing the formation of endothelial cell pseudopods. Also, the internalized hyphae were surrounded by a loose network of microfilaments. In contrast, A. fumigatus hyphae invaded the luminal endothelial cell surface by inducing by the formation of endothelial cell pseudopods. These endocytosed hyphae were surrounded by a tight network of microfilaments. Abluminal infection induced greater E-selectin, IL-8, tissue factor and TNF-alpha gene expression, but less endothelial cell damage than did luminal infection. Endothelial cell stimulation by infection of either surface was mediated by endothelial cell-derived TNF-alpha, and was not influenced by gliotoxin secreted by A. fumigatus. These differences in the endothelial cell response to abluminal versus luminal infection may contribute to differences in the pathogenesis of invasive versus haematogenously disseminated aspergillosis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interactions of Aspergillus fumigatus with vascular endothelial cells.Med Mycol. 2006 Sep;44 Suppl 1:S115-7. doi: 10.1080/13693780600897989. Med Mycol. 2006. PMID: 17050430
-
Aspergillus fumigatus stimulates leukocyte adhesion molecules and cytokine production by endothelial cells in vitro and during invasive pulmonary disease.Infect Immun. 2008 Aug;76(8):3429-38. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01510-07. Epub 2008 May 19. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18490455 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of Aspergillus fumigatus with endothelial cells: internalization, injury, and stimulation of tissue factor activity.Blood. 2004 Mar 15;103(6):2143-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-06-2186. Epub 2003 Nov 20. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14630829
-
Fungal invasion of normally non-phagocytic host cells.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Dec;2(12):e129. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020129. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 17196036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of electron microscopy and solid-state NMR analysis for new views and compositional parameters of Aspergillus fumigatus biofilms.Med Mycol. 2019 Apr 1;57(Supplement_2):S239-S244. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myy140. Med Mycol. 2019. PMID: 30816969 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in Invasive Aspergillosis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009 Jul;22(3):447-65. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00055-08. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19597008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin Combined with Liposomal Amphotericin B Improves Outcome during Disseminated Aspergillosis in Mice.Front Immunol. 2014 Oct 14;5:502. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00502. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25352847 Free PMC article.
-
Are respiratory complications more likely in patients with pulmonary aspergillosis treated with echinocandins in the setting of neutrophil influx?Virulence. 2014 Apr 1;5(3):375-7. doi: 10.4161/viru.28291. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Virulence. 2014. PMID: 24569451 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of Aspergillus fumigatus DvrA in host cell interactions and virulence.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Oct;9(10):1432-40. doi: 10.1128/EC.00055-10. Epub 2010 Jul 30. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20675576 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Models for Studying Respiratory Host-Pathogen Interactions.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2021 Jun;5(6):e2000624. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202000624. Epub 2021 May 4. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 33943040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

