Social approach in genetically engineered mouse lines relevant to autism
- PMID: 19016890
- PMCID: PMC2659808
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2008.00452.x
Social approach in genetically engineered mouse lines relevant to autism
Abstract
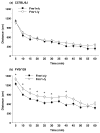
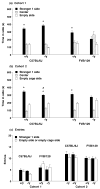
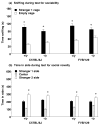
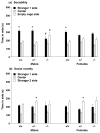
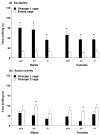
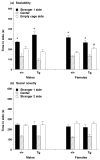
Profound impairment in social interaction is a core symptom of autism, a severe neurodevelopmental disorder. Deficits can include a lack of interest in social contact and low levels of approach and proximity to other children. In this study, a three-chambered choice task was used to evaluate sociability and social novelty preference in five lines of mice with mutations in genes implicated in autism spectrum disorders. Fmr1(tm1Cgr/Y)(Fmr1(-/y)) mice represent a model for fragile X, a mental retardation syndrome that is partially comorbid with autism. We tested Fmr1(-/y)mice on two genetic backgrounds, C57BL/6J and FVB/N-129/OlaHsd (FVB/129). Targeted disruption of Fmr1 resulted in low sociability on one measure, but only when the mutation was expressed on FVB/129. Autism has been associated with altered serotonin levels and polymorphisms in SLC6A4 (SERT), the serotonin transporter gene. Male mice with targeted disruption of Slc6a4 displayed significantly less sociability than wild-type controls. Mice with conditional overexpression of Igf-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1) offered a model for brain overgrowth associated with autism. Igf-1 transgenic mice engaged in levels of social approach similar to wild-type controls. Targeted disruption in other genes of interest, En2 (engrailed-2) and Dhcr7, was carried on genetic backgrounds that showed low levels of exploration in the choice task, precluding meaningful interpretations of social behavior scores. Overall, results show that loss of Fmr1 or Slc6a4 gene function can lead to deficits in sociability. Findings from the fragile X model suggest that the FVB/129 background confers enhanced susceptibility to consequences of Fmr1 mutation on social approach.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GSK3 influences social preference and anxiety-related behaviors during social interaction in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome and autism.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 16;5(3):e9706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009706. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20300527 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic-background modulation of core and variable autistic-like symptoms in Fmr1 knock-out mice.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 22;6(2):e17073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017073. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21364941 Free PMC article.
-
Sociability and preference for social novelty in five inbred strains: an approach to assess autistic-like behavior in mice.Genes Brain Behav. 2004 Oct;3(5):287-302. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-1848.2004.00076.x. Genes Brain Behav. 2004. PMID: 15344922
-
Social behavior phenotypes in fragile X syndrome, autism, and the Fmr1 knockout mouse: theoretical comment on McNaughton et al. (2008).Behav Neurosci. 2008 Apr;122(2):483-9. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.122.2.483. Behav Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18410188 Review.
-
Monogenic mouse models of social dysfunction: implications for autism.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Aug 15;251:75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23327738 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of Rett syndrome (RTT) with induced pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cell Investig. 2016 Sep 28;3:52. doi: 10.21037/sci.2016.09.05. eCollection 2016. Stem Cell Investig. 2016. PMID: 27777941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of social approach by MK-801, amphetamine, and fluoxetine in adolescent C57BL/6J mice.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2013 Mar-Apr;36:36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2012.07.007. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2013. PMID: 22898204 Free PMC article.
-
Ucn3 and CRF-R2 in the medial amygdala regulate complex social dynamics.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Nov;19(11):1489-1496. doi: 10.1038/nn.4346. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27428651
-
GSK3 influences social preference and anxiety-related behaviors during social interaction in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome and autism.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 16;5(3):e9706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009706. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20300527 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Social Dominance and Altered Neuronal Excitability in the Prefrontal Cortex of Male KCC2b Mutant Mice.Autism Res. 2019 May;12(5):732-743. doi: 10.1002/aur.2098. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Autism Res. 2019. PMID: 30977597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000.
-
- Anderson GM, Horne WC, Chatterjee D, Cohen DJ. The hyperserotonemia of autism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:331–340. discussion 341–332. - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Minshew NJ, Field K, Sparks BF, Singh N. Effects of age on brain volume and head circumference in autism. Neurology. 2002;59:175–183. - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E, Rutter M. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med. 1995;25:63–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

