The decrease of regulatory T cells correlates with excessive activation and apoptosis of CD8+ T cells in HIV-1-infected typical progressors, but not in long-term non-progressors
- PMID: 19016904
- PMCID: PMC2753909
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02978.x
The decrease of regulatory T cells correlates with excessive activation and apoptosis of CD8+ T cells in HIV-1-infected typical progressors, but not in long-term non-progressors
Abstract
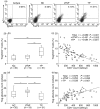
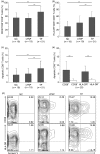
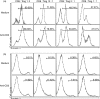
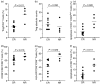
Persistent HIV infection results in a decrease in absolute counts of CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells (Treg). To investigate the role of decreased Treg counts in the regulation of excessive activation and apoptosis of CD8(+) T cells in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infection, we characterized Treg in 83 HIV-1-infected individuals, including 19 long-term non-progressors (LTNPs) and 51 typical progressors (TPs) who were treatment-naïve, and 13 AIDS patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), of whom nine were complete responders (CRs) and the remaining four were non-responders (NRs) to the treatment. TPs but not LTNPs had a significant decrease in absolute counts of circulating Treg, which was inversely correlated with the activation and apoptosis of CD8(+) T cells. Efficient HAART was found to increase Treg counts in CR patients and temper the excessive activation and apoptosis of CD8(+) T cells. Moreover, isolated Treg significantly inhibited the spontaneous and anti-CD3-induced apoptosis of CD8(+) T cells in a dose-dependent manner in vitro. Thus, our findings indicate that the decrease in Treg closely correlates with the increase in apoptotic CD8(+) T cells and disease progression in chronic HIV-1 infection, and that Treg may play a key role in maintaining the balance between the amount and quality of CD8(+) T cells in HIV-1 infection. Manipulation of Treg function may be a promising strategy for immune therapy of this disease.
Figures

References
-
- Douek DC, Brenchley JM, Betts MR, et al. HIV preferentially infects HIV-specific CD4+ T cells. Nature. 2002;417:95–8. - PubMed
-
- Gougeon ML, Lecoeur H, Dulioust A, Enouf MG, Crouvoiser M, Goujard C, Debord T, Montagnier L. Programmed cell death in peripheral lymphocytes from HIV-infected persons: increased susceptibility to apoptosis of CD4 and CD8 T cells correlates with lymphocyte activation and with disease progression. J Immunol. 1996;156:3509–20. - PubMed
-
- Muro-Cacho CA, Pantaleo G, Fauci AS. Analysis of apoptosis in lymph nodes of HIV-infected persons. Intensity of apoptosis correlates with the general state of activation of the lymphoid tissue and not with stage of disease or viral burden. J Immunol. 1995;154:5555–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

