Eosinophil granules function extracellularly as receptor-mediated secretory organelles
- PMID: 19017810
- PMCID: PMC2587599
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0804547105
Eosinophil granules function extracellularly as receptor-mediated secretory organelles
Abstract
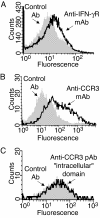
Intracellular granules in several types of leukocytes contain preformed proteins whose secretions contribute to immune and inflammatory functions of leukocytes, including eosinophils, cells notably associated with asthma, allergic inflammation, and helminthic infections. Cytokines and chemokines typically elicit extracellular secretion of granule proteins by engaging receptors expressed externally on the plasma membranes of cells, including eosinophils. Eosinophil granules, in addition to being intracellular organelles, are found as intact membrane-bound structures extracellularly in tissue sites of eosinophil-associated diseases. Neither the secretory capacities of cell-free eosinophil granules nor the presence of functional cytokine and chemokine receptors on membranes of leukocyte granules have been recognized. Here, we show that granules of human eosinophils express membrane receptors for a cytokine, IFN-gamma, and G protein-coupled membrane receptors for a chemokine, eotaxin, and that these receptors function by activating signal-transducing pathways within granules to elicit secretion from within granules. Capacities of intracellular granule organelles to function autonomously outside of eosinophils as independent, ligand-responsive, secretion-competent structures constitute a novel postcytolytic mechanism for regulated secretion of eosinophil granule proteins that may contribute to eosinophil-mediated inflammation and immunomodulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional extracellular eosinophil granules: novel implications in eosinophil immunobiology.Curr Opin Immunol. 2009 Dec;21(6):694-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.07.011. Epub 2009 Aug 24. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19709867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteinyl leukotrienes acting via granule membrane-expressed receptors elicit secretion from within cell-free human eosinophil granules.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Feb;125(2):477-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.029. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20159258 Free PMC article.
-
Intragranular vesiculotubular compartments are involved in piecemeal degranulation by activated human eosinophils.Traffic. 2005 Oct;6(10):866-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00322.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 16138901 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle-mediated secretion of human eosinophil granule-derived major basic protein.Lab Invest. 2009 Jul;89(7):769-81. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2009.40. Epub 2009 Apr 27. Lab Invest. 2009. PMID: 19398958 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophil secretion of granule-derived cytokines.Front Immunol. 2014 Oct 27;5:496. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00496. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25386174 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eosinophil-derived cytokines in health and disease: unraveling novel mechanisms of selective secretion.Allergy. 2013 Mar;68(3):274-84. doi: 10.1111/all.12103. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23347072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal eosinophils, homeostasis and response to bacterial intrusion.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Jun;43(3):295-306. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00856-x. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 33929602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Location of eosinophils in the airway wall is critical for specific features of airway hyperresponsiveness and T2 inflammation in asthma.Eur Respir J. 2022 Aug 4;60(2):2101865. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01865-2021. Print 2022 Aug. Eur Respir J. 2022. PMID: 35027395 Free PMC article.
-
How to detect eosinophil ETosis (EETosis) and extracellular traps.Allergol Int. 2021 Jan;70(1):19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Allergol Int. 2021. PMID: 33189567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional extracellular eosinophil granules: novel implications in eosinophil immunobiology.Curr Opin Immunol. 2009 Dec;21(6):694-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.07.011. Epub 2009 Aug 24. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19709867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Klion AD, Nutman TB. The role of eosinophils in host defense against helminth parasites. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:30–37. - PubMed
-
- Kay AB. The role of eosinophils in the pathogenesis of asthma. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11:148–152. - PubMed
-
- Lee JJ, Lee NA. Eosinophil degranulation: An evolutionary vestige or a universally destructive effector function? Clin Exp Allergy. 2005;35:986–994. - PubMed
-
- Moqbel R, Coughlin JJ. Differential secretion of cytokines. Sci STKE. 2006;2006:pe26. - PubMed
-
- Lacy P, et al. Rapid mobilization of intracellularly stored RANTES in response to interferon-gamma in human eosinophils. Blood. 1999;94:23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

