Programmed upregulation of adipogenic transcription factors in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring
- PMID: 19017816
- PMCID: PMC3444244
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719108318597
Programmed upregulation of adipogenic transcription factors in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring
Abstract
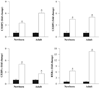
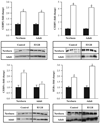
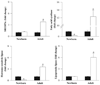
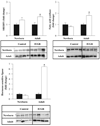
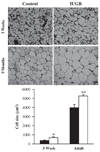
As enhanced adipogenesis contributes to programmed obesity, adipogenic and lipogenic signaling pathways in intrauterine growth restricted (IUGR) offspring were examined. From 10 days to term gestation, rats received ad libitum food (control) or were 50% food-restricted (IUGR). Pups were nursed and weaned to ad libitum diet. mRNA and protein levels of adipogenic transcription factors and lipid enzymes (1 day and 9 month) and adipocyte cell size (3 weeks and 9 months) were determined. One day-old IUGR males showed upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR gamma(2)), including upstream factors regulating PPAR gamma, and RXR alpha, with which PPAR gamma heterodimerizes. Intracellular lipolytic enzyme (hormone-sensitive lipase) was downregulated. Nine-month-old IUGR males showed upregulation of adipogenic and lipogenic (SREBP1c) transcription factors with upregulation of enzymes facilitating fatty acid uptake (lipoprotein lipase) and synthesis (fatty acid synthase), leading to hypertrophic adipocytes. Paradoxical upregulation of adipogenesis signaling cascade prior to the development of obesity in IUGR males suggests early changes in signaling mechanisms.
Figures

References
-
- Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2087–2102. - PubMed
-
- Plagemann A, Harder T. The changing face and implications of childhood obesity. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2414–2416. - PubMed
-
- Reilly MP, Rader DJ. The metabolic syndrome: more than the sum of its parts? Circulation. 2003;108:1546–1551. - PubMed
-
- Spiegelman BM, Flier JS. Adipogenesis and obesity: rounding out the big picture. Cell. 1996;87:377–389. - PubMed
-
- Ailhaud G, Grimaldi P, Negrel R. Cellular and molecular aspects of adipose tissue development. Annu Rev Nutr. 1992;12:207–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

