Relationship of treatment-related cytopenias and response to lenalidomide in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
- PMID: 19018091
- PMCID: PMC2645116
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.5770
Relationship of treatment-related cytopenias and response to lenalidomide in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) often require treatment with growth factors (GFs) or non-GF therapies. One non-GF drug, lenalidomide, is particularly effective at achieving transfusion independence (TI) in patients with lower-risk MDS with the del(5q) cytogenetic abnormality. However, approximately half of del(5q) patients and one quarter of non-del(5q) patients treated with lenalidomide experience significant cytopenias. Lenalidomide-induced cytopenias occurring early in treatment may serve as a surrogate marker of clonal suppression and, therefore, may be predictive of a TI response.
Patients and methods: We analyzed 362 low-risk, transfusion-dependent patients with MDS, with or without the del(5q) abnormality, enrolled in two phase II studies (MDS-003 and MDS-002) to determine whether treatment-related cytopenias are correlated with lenalidomide response. Cytopenias were assessed during the first 8 weeks of therapy, and response was defined as TI; response predictors were explored in univariate and multivariate analyses.
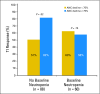
Results: Among patients with del(5q), 70% of those whose platelet count decreased by > or = 50% achieved TI, as compared with 42% of those whose platelet count remained stable or declined by less than 50% (P = .01). Among patients without baseline neutropenia, 82% of those whose absolute neutrophil count (ANC) decreased by > or = 75% achieved TI, as compared with 51% whose ANC remained stable or decreased by less than 75% (P = .02). These relationships were consistent in multivariate analyses. No relationship between the development of cytopenias and response could be established for lower-risk patients with MDS without del(5q).
Conclusion: These findings support the hypothesis that a direct cytotoxic effect of lenalidomide specific to the del(5q) clone may be indicative of a TI response.
Figures

References
-
- List AF, Vardiman J, Issa JP, et al: Myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 297-317, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, et al: The World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: Report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting, Airlie House, Virginia, November, 1997. Ann Oncol 10:1419-1432, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Ma X, Does M, Raza A, et al: Myelodysplastic syndromes: Incidence and survival in the United States. Cancer 109:1536-1542, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Rollison DE, Hayat M, Smith M, et al: First report of national estimates of the incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myeloproliferative disorders from the U.S. SEER Program. Blood 108:77a, 2006. (suppl; abstr 247)
-
- Sekeres MA, Kantarjian H, List A, et al: P127 Prospective cross-sectional analysis of cytopenias and transfusion needs of MDS patients in the USA. Leuk Res 31:S108, 2007. (suppl 1)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

