Sensitive detection of colorectal cancer in peripheral blood by septin 9 DNA methylation assay
- PMID: 19018278
- PMCID: PMC2582436
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003759
Sensitive detection of colorectal cancer in peripheral blood by septin 9 DNA methylation assay
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths despite the fact that detection of this cancer in early stages results in over 90% survival rate. Currently less than 45% of at-risk individuals in the US are screened regularly, exposing a need for better screening tests. We performed two case-control studies to validate a blood-based test that identifies methylated DNA in plasma from all stages of CRC.
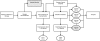
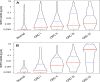
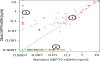
Methodology/principal findings: Using a PCR assay for analysis of Septin 9 (SEPT9) hypermethylation in DNA extracted from plasma, clinical performance was optimized on 354 samples (252 CRC, 102 controls) and validated in a blinded, independent study of 309 samples (126 CRC, 183 controls). 168 polyps and 411 additional disease controls were also evaluated. Based on the training study SEPT9-based classification detected 120/252 CRCs (48%) and 7/102 controls (7%). In the test study 73/126 CRCs (58%) and 18/183 control samples (10%) were positive for SEPT9 validating the training set results. Inclusion of an additional measurement replicate increased the sensitivity of the assay in the testing set to 72% (90/125 CRCs detected) while maintaining 90% specificity (19/183 for controls). Positive rates for plasmas from the other cancers (11/96) and non-cancerous conditions (41/315) were low. The rate of polyp detection (>1 cm) was approximately 20%.
Conclusions/significance: Analysis of SEPT9 DNA methylation in plasma represents a straightforward, minimally invasive method to detect all stages of CRC with potential to satisfy unmet needs for increased compliance in the screening population. Further clinical testing is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mandel JS, Church TR, Ederer F, Bond JH. Colorectal cancer mortality: effectiveness of biennial screening for fecal occult blood. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91:434–437. - PubMed
-
- Fisher JA, Fikry C, Troxel AB. Cutting cost and increasing access to colorectal cancer screening: another approach to following the guidelines. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:108–113. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Wang H, Hu J, Li N, Liu Y, et al. New immunochemical fecal occult blood test with two-consecutive stool sample testing is a cost-effective approach for colon cancer screening: results of a prospective multicenter study in Chinese patients. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:3078–3083. - PubMed
-
- Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, Turnbull BA, Ross ME. Fecal DNA versus fecal occult blood for colorectal-cancer screening in an average-risk population. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2704–2714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

