Identification of differentially expressed root genes upon rhizomania disease
- PMID: 19019003
- PMCID: PMC6640463
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2008.00498.x
Identification of differentially expressed root genes upon rhizomania disease
Abstract
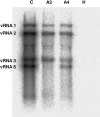
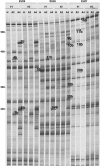
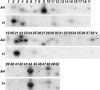
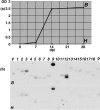
Rhizomania is one of the most devastating sugar beet diseases. It is caused by Beet necrotic yellow vein virus (BNYVV), which induces abnormal rootlet proliferation. To understand better the physiological and molecular basis of the disorder, transcriptome analysis was performed by restriction fragment differential display polymerase chain reaction (RFDD-PCR), which provided differential gene expression profiles between non-infected and infected sugar beet roots. Two distinct viral isolates were used to detect specific or general virus-induced genes. Differentially expressed genes were selected and identified by sequence analysis, followed by reverse Northern and reverse transcriptase PCR experiments. These latter analyses of different plants (Beta vulgaris and Beta macrocarpa) infected under distinct standardized conditions revealed specific and variable expressions. Candidate genes were linked to cell development, metabolism, defence signalling and oxidative stress. In addition, the expression of already characterized genes linked to defence response (pathogenesis-related protein genes), auxin signalling and cell elongation was also studied to further examine some aspects of the disease. Differential expression was retrieved in both B. vulgaris and B. macrocarpa. However, some candidate genes were found to be deregulated in only one plant species, suggesting differential response to BNYVV or specific responses to the BNYVV vector.
Figures

References
-
- Burketova, L. , Stillerova, K. and Feltlova, M. (2003) Immunohistological localization of chitinase and beta‐1,3‐glucanase in rhizomania‐diseased and benzothiadiazole treated sugar beet roots. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 63, 47–54.
-
- Cassab, G.I. (1998) Plant cell wall proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49, 281–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

